OECD broadband matures: fibre and 5G scale-up
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) data shows fixed and mobile broadband have shifted from build-out to scale-up, with fibre and 5G underpinning a new phase of digital infrastructure.
2019–2024 OECD broadband by the numbers
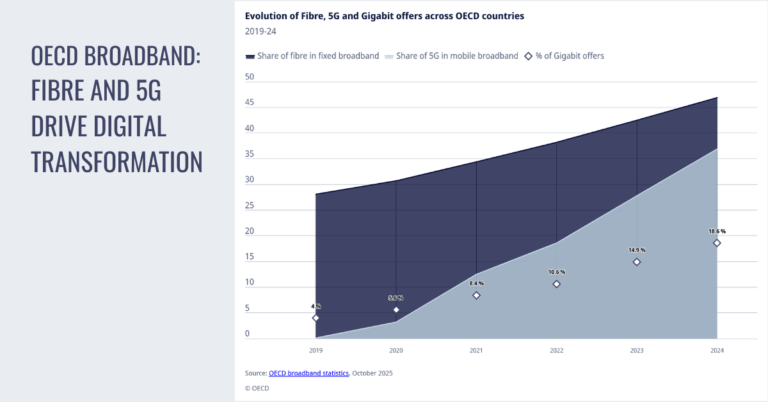
Fixed broadband penetration across the OECD rose to 36.5 subscriptions per 100 inhabitants by end-2024, up from 32 in 2019, while the fibre share of fixed lines jumped from 28 percent to 47 percent over the same period. Gigabit-tier offers (≥1 Gbps) moved from 4 percent of subscriptions in 2019 to 19 percent in 2024, signaling both wider availability and growing appetite for very high throughput. On mobile, average monthly data consumption per subscription increased 2.5x—from 6 GB at end-2019 to 15 GB in 2024—aligned with more video, cloud, and AI-assisted applications shifting to handhelds and connected devices.
Evolving demand: hybrid work, AI, and immersive apps
Pandemic-era behaviors—remote and hybrid work, cloud-first IT, and digital services at scale—have persisted and intensified, while new workloads such as generative AI, immersive applications, and proliferating IoT endpoints add pressure for low-latency, high-reliability access. This reinforces the need for dense fibre backbones, 5G capacity and coverage, and diversified access options where fibre-to-the-premises is uneconomic.
Fibre backbone for next-gen broadband and 5G
Fibre’s expansion is both a stand-alone consumer play and the critical substrate for 5G densification, edge computing, and wholesale access models.
Fibre penetration and share gains
Fibre now represents nearly half of all fixed broadband subscriptions across the OECD, up 19 percentage points since 2019. That shift replaces aging copper loops, improves symmetry and latency, and lowers energy per bit—benefits that compound when fibre is used for 5G fronthaul/backhaul and enterprise connectivity. The gigabit adoption curve suggests households and SMEs increasingly value headroom for concurrent video, collaboration, and AI-enabled workflows.
Fibre leaders and market playbooks
Several OECD markets have crossed the 80 percent fibre share threshold: Iceland (93 percent), Korea (90.5 percent), Spain (89 percent), Finland (81.6 percent), and Lithuania (80.7 percent). Their playbooks blend sustained civil-works execution, favorable permitting, and aggressive copper switch-off timelines. For markets still below the OECD average, the lesson is clear: the economics improve when fibre builds are coordinated with utility digs, supported by predictable rights-of-way, and paired with take-up programs that accelerate migration from legacy tiers.
Strategy: build, buy, or share networks
As markets mature, operators face tougher capital allocation choices: extend fibre to new areas, acquire or consolidate alternative network (altnet) footprints, or scale through wholesale and shared infrastructure. Open-access models can improve utilization and reduce duplicated digs; in dense urban areas, wholesale-only fibre and bitstream products can enable retail competition without undermining investment. Policymakers can help by streamlining permits, harmonizing building codes for in-building wiring, and tying subsidies to measurable coverage, quality, and affordability outcomes.
5G, FWA, and LEO reshape broadband access
Mobile networks, fixed wireless access, and new satellite constellations are complementing fibre to close gaps, add redundancy, and compete on speed-to-serve.
5G capacity, coverage, and traffic growth
The 2.5x rise in mobile data per subscription underscores the value of mid-band spectrum, densification, and cloud-native 5G cores as operators move to richer services. As 5G-Advanced capabilities mature, performance features such as improved uplink, positioning, and network automation will support enterprise use cases, but economics still hinge on efficient spectrum use and fibreised backhaul. For many operators, selective small-cell deployments and street-level fibre become the bottleneck and the opportunity.
Fixed wireless access’s growing role
Fixed wireless access has matured into a mainstream access option in suburban and rural areas, using excess 5G capacity to deliver competitive broadband where fibre is scarce or slow to arrive. It is a powerful go-to-market lever for rapid subscriber growth, yet it requires disciplined traffic engineering to avoid congestion at peak times and careful alignment of tariffs with usage to protect mobile quality of experience. In fibre-rich urban cores, FWA is more of a tactical overlay or backup.
LEO satellites close coverage gaps
LEO-based satellite broadband improves reach and service consistency for sparsely populated regions, maritime, and remote industrial sites, and can backstop resilience for enterprises. Capacity constraints, terminal costs, and weather susceptibility remain considerations, but integration into universal service frameworks and enterprise SD-WAN designs is advancing, especially when paired with terrestrial links for failover.
Monetizing broadband with quality and energy efficiency
As access markets mature, competition shifts from raw coverage to quality, differentiation, and unit economics.
Converting gigabit demand into ARPU
The surge in gigabit subscriptions does not automatically translate into higher ARPU unless packaging evolves. Tiered speed plus quality-of-experience promises, symmetrical uplink for creators and SMBs, latency-sensitive add-ons for gaming and collaboration, and converged fixed-mobile bundles can unlock willingness to pay. Enterprise offers should emphasize deterministic performance and APIs that expose network capabilities into IT workflows.
Competing on latency, reliability, and SLAs
Latency, jitter, uptime, and repair intervals increasingly decide winners as applications grow interactive and time-sensitive. Publishing transparent quality metrics, offering clear SLAs, and using standards-based measurement (e.g., from recognized bodies in broadband and mobile performance) can build trust with B2B buyers and support premium tiers. Edge caching and local breakouts further reduce latency for AI inference and real-time media.
Energy efficiency and capex discipline
Fibre and modern 5G radios lower energy per bit relative to legacy copper and 3G/4G-only footprints, which supports sustainability goals and operating margins. Priorities include copper switch-off to decommission power-hungry assets, RAN energy-saving features, and targeted build programs that raise utilization—often through shared infrastructure and wholesale partnerships.
Action plan for operators and policymakers
The next phase is about translating coverage into competitive advantage and inclusive growth.
Operator priorities for fibre, 5G, and FWA
Accelerate fibre rollouts where take-up is probable, sequencing builds with migration incentives to retire copper faster. Use data-driven FWA deployment rules to fill coverage gaps while protecting mobile QoE, and integrate LEO as a resilience option for enterprise and public sector contracts. Differentiate with low-latency and symmetric tiers, converge fixed and mobile offers, and expose network capabilities through APIs for partners in cloud, gaming, and industrial IoT. Maintain capex discipline via network sharing, wholesale monetization, and automation across planning, provisioning, and assurance.
Policy levers for investment and competition
Streamline permits and dig-once policies to reduce rollout time and cost, support building access rules for fibre-ready homes, and tie public funding to verifiable performance and affordability. Ensure timely, technology-neutral spectrum licensing with clear renewal terms, and promote fair wholesale frameworks that encourage investment while enabling competition. Transparency around quality metrics and protection for vulnerable users can widen adoption without distorting markets.
OECD broadband trends to watch through 2026
A handful of indicators will signal whether OECD markets are converting infrastructure gains into productivity and growth.
Signals of progress and digital competitiveness
Watch the mix of gigabit subscriptions and actual usage patterns, fibre take-up versus homes passed, the pace of 5G standalone core adoption, and the share of traffic carried by FWA relative to mobile handsets. Track consolidation among altnets and the evolution of open-access wholesale models. Monitor enterprise demand for low-latency SLAs and API-enabled services, and the role of LEO in universal service and SD-WAN portfolios. Markets that align these vectors fastest will set the benchmark for digital competitiveness in the OECD.