News
- April 11, 2024
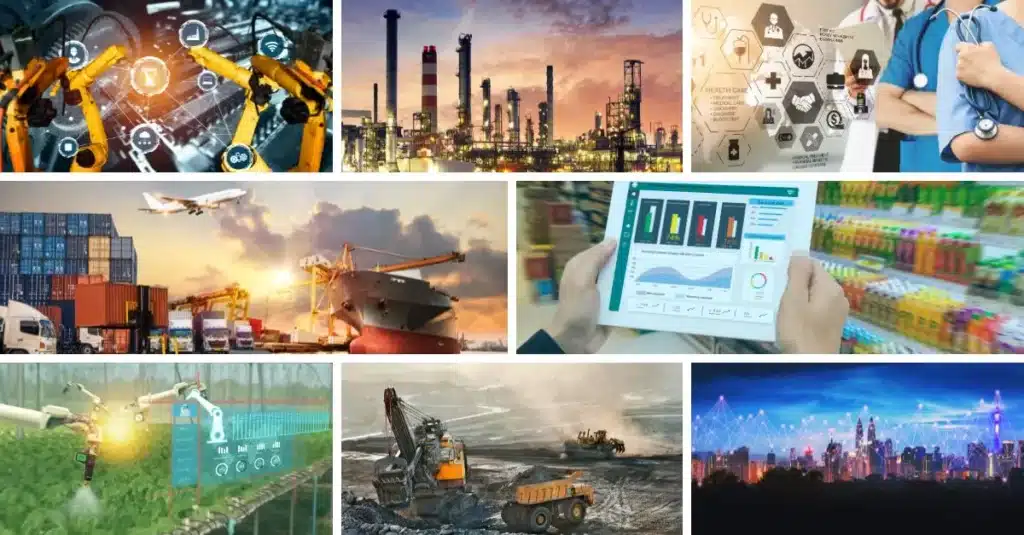
Panasonic Connect Europe has launched a new private 5G network facility in Munich, enhancing telecom services for businesses across various sectors. This hub aims to streamline private network management and deployment, showcasing Panasonic’s commitment to advanced connectivity solutions.
News
- April 11, 2024
Panasonic Connect Europe has launched a new private 5G network facility in Munich, enhancing telecom services for businesses across various sectors. This hub aims to streamline private network management and deployment, showcasing Panasonic’s commitment to advanced connectivity solutions.