Musk and Ambani Compete for India’s Satellite Broadband Market
India’s new satellite spectrum allocation policy could reshape its telecom sector, according to Telecommunications Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia. The government’s decision to allocate satellite spectrum administratively—rather than through auctions—has already sparked a clash between Elon Musk’s Starlink and Mukesh Ambani’s Reliance Jio. While the approach aims to attract global companies like Amazon and SpaceX, it has also raised concerns among Indian telecom giants about maintaining a level playing field.
Reliance Jio, which invested $19 billion in airwave auctions, argues that administrative spectrum allocation could create an unfair advantage for satellite broadband providers. However, Scindia defended the government’s stance, saying the goal is to provide consumers with more choices in connectivity solutions.
Administrative Allocation Supports Global Standards
The Indian government’s decision aligns with global trends, where satellite spectrum is often allocated administratively. Analysts believe an auction-based approach would have required higher investments, potentially discouraging foreign players like Starlink and Amazon Kuiper from entering the Indian market.
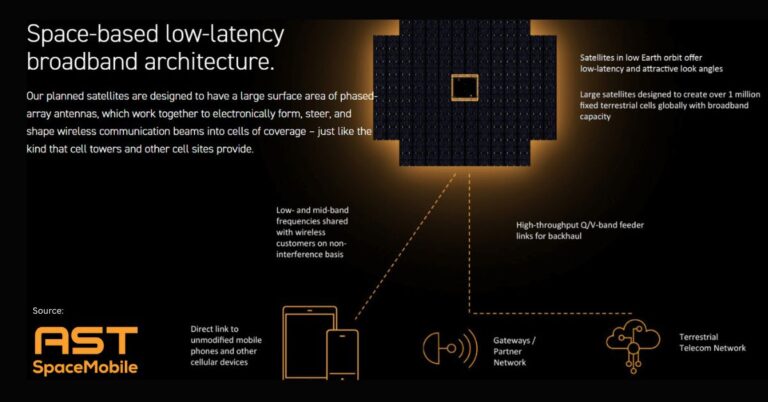
Starlink, which has been seeking entry into India, could provide high-speed satellite broadband services across rural and remote areas. On the other hand, Ambani’s Jio worries that satellite players could attract not just broadband customers but also disrupt the telecom landscape by eventually offering data and voice services.
“My job as telecoms minister is to make sure that you have as many choices as possible,” Scindia said in an interview. When asked about Reliance’s concerns, he highlighted the evolving nature of technology and emphasized the need for companies to adapt.
Limitations of Current Satellite Technology
Scindia noted that existing satellite technology has limitations. For instance, devices using satellite broadband require a clear line of sight to the sky, making it impractical for indoor usage. Terrestrial networks, which can deliver seamless indoor coverage, remain essential for everyday connectivity. “The minute you come into this building, you’re done,” he explained, emphasizing that satellite broadband cannot yet replace traditional networks entirely.
India’s Growing Telecom Market Attracts Global Players
India, with its 942 million telecom users, is one of the largest and most competitive telecom markets in the world. Companies like Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel, and Vodafone Idea dominate the market, offering some of the world’s lowest data prices.
Despite this intense competition, the satellite broadband market in India is gaining momentum. Deloitte predicts the sector will be worth $1.9 billion by 2030, driven by demand for connectivity in underserved regions. Companies such as Starlink and Amazon Kuiper are seeking licenses to tap into this market, but their applications are still under review by the Indian government.
Musk’s Pricing Strategy Disrupts Markets Globally
Elon Musk’s Starlink has gained a reputation for disrupting markets with aggressive pricing strategies. For example, in Kenya, Starlink slashed its subscription cost to $10 per month, compared to $120 in the U.S., forcing local telecom providers to rethink their pricing models. This track record is raising questions about how Musk’s entry could impact India’s telecom ecosystem.
Challenges for Domestic Telecom Operators
While India’s satellite spectrum policy aims to foster competition, it also poses challenges for domestic players. Vodafone Idea, in which the Indian government owns a stake, continues to struggle with a massive $24 billion debt. Scindia declined to comment on whether the government would offer further relief to the company but acknowledged the importance of reviving the state-run Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL).
BSNL, once a dominant player, has lost significant market share due to intense competition. However, the government is supporting its expansion into 4G services to regain relevance. BSNL currently has 99 million users and remains a critical part of India’s telecom strategy.
Balancing Competition and Consumer Choice
The Indian government’s satellite spectrum policy reflects its broader vision of enhancing digital connectivity while fostering competition. By opening the doors to global players like Starlink and Amazon Kuiper, the government aims to expand internet access in underserved regions. However, balancing the interests of domestic telecom operators and new entrants will remain a challenge.
As India’s telecom landscape evolves, companies will need to adapt to changing technologies and consumer demands. With the satellite broadband market poised for growth, the competition between Reliance Jio, Starlink, and other players could drive innovation and improve connectivity for millions of users.