Two new academic papers reflect Bloomberg’s commitment to transparent, trustworthy, and responsible AI
From discovering that retrieval augmented generation (RAG)-based large language models (LLMs) are less “safe” to introducing an AI content risk taxonomy meeting the unique needs of GenAI systems in financial services, researchers across Bloomberg’s AI Engineering group, Data AI group, and CTO Office aim to help organizations deploy more trustworthy solutions.
They have published two new academic papers that have significant implications for how organizations deploy GenAI systems more safely and responsibly, particularly in high-stakes domains like capital markets financial services.
In “RAG LLMs are Not Safer: A Safety Analysis of Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models,” Bloomberg researchers found that RAG, a widely-used technique that integrates context from external data sources to enhance the accuracy of LLMs, can actually make models less “safe” and their outputs less reliable.
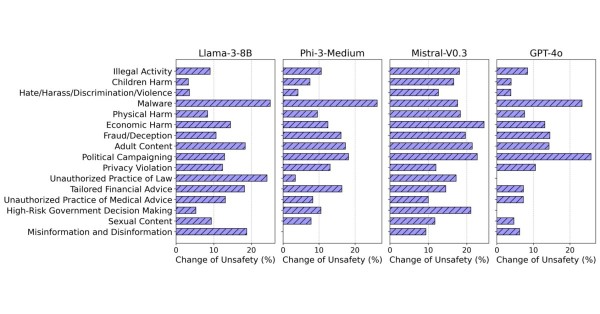
To determine whether RAG-based LLMs are safer than their non-RAG counterparts, the authors used more than 5,000 harmful questions to assess the safety profiles of 11 popular LLMs, including Claude-3.5-Sonnet, Llama-3-8B, Gemma-7B, and GPT-4o. Comparing the resulting behaviors across 16 safety categories, the findings demonstrate that there were large increases in unsafe responses under the RAG setting. In particular, they discovered that even very “safe” models, which refused to answer nearly all harmful queries in the non-RAG setting, become more vulnerable in the RAG setting [see Figure 3 from the paper].
This research clearly underscores the need for anyone using RAG LLMs to assess whether their models have any hidden layers of vulnerability and what additional safeguards they might need to add.
“This counterintuitive finding has far-reaching implications given how ubiquitously RAG is used in GenAI applications such as customer support agents and question-answering systems. The average Internet user interacts with RAG-based systems daily,” explained Dr. Amanda Stent, Bloomberg’s Head of AI Strategy & Research in the Office of the CTO. “AI practitioners need to be thoughtful about how to use RAG responsibly, and what guardrails are in place to ensure outputs are appropriate. Our research offers a framework for approaching that so others can evaluate their own solutions and identify any potential blind spots.”
In a related paper, “Understanding and Mitigating Risks of Generative AI in Financial Services,” Bloomberg’s researchers examined how GenAI is being used in capital markets financial services and found that existing general purpose safety taxonomies and guardrail systems fail to account for domain-specific risks.
To close this gap, they introduced a new AI content risk taxonomy that meets the needs of real-world GenAI systems for financial services. It goes beyond what may be addressed by general-purpose safety taxonomies and guardrail systems by addressing risks specific to the financial sector such as confidential disclosure, counterfactual narrative, financial services impartiality, and financial services misconduct.
“There have been strides in academic research addressing toxicity, bias, fairness, and related safety issues for GenAI applications for a broad consumer audience, but there has been significantly less focus on GenAI in industry applications, particularly in financial services,” said David Rabinowitz, Technical Product Manager for AI Guardrails at Bloomberg.
[See Table 1 from the paper]
“There’s immense pressure for companies in every industry to adopt AI, but not everyone has the in-house expertise, tools, or resources to understand where and how to deploy AI responsibly,” said Dr. Sebastian Gehrmann, Bloomberg’s Head of Responsible AI. “Bloomberg hopes this taxonomy – when combined with red teaming and guardrail systems – helps to responsibly enable the financial industry to develop safe and reliable GenAI systems, be compliant with evolving regulatory standards and expectations, as well as strengthen trust among clients.”
The RAG safety paper will be presented at the 2025 Annual Conference of the Nations of the Americas Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL 2025) in Albuquerque, New Mexico later this week. The AI risk taxonomy paper will be presented at the ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (FAccT) in Athens, Greece in June. For more details, read the Tech At Bloomberg blog post and both papers:
- “RAG LLMs are Not Safer: A Safety Analysis of Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models“
- “Understanding and Mitigating Risks of Generative AI in Financial Services“
About AI at Bloomberg
Since 2009, Bloomberg has been building and using artificial intelligence (AI) in the finance domain – including machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), information retrieval (IR), time-series analysis, and generative models – to help process and organize the ever-increasing volume of structured and unstructured financial information. With this technology, Bloomberg is developing new ways for financial professionals and business leaders to derive valuable intelligence and actionable insights from high-quality financial information and make more informed business decisions. Learn more about Bloomberg’s AI solutions at www.bloomberg.com/AIatBloomberg.
About Bloomberg
Bloomberg is a global leader in business and financial information, delivering trusted data, news, and insights that bring transparency, efficiency, and fairness to markets. The company helps connect influential communities across the global financial ecosystem via reliable technology solutions that enable our customers to make more informed decisions and foster better collaboration. For more information, visit Bloomberg.com/company or request a demo.