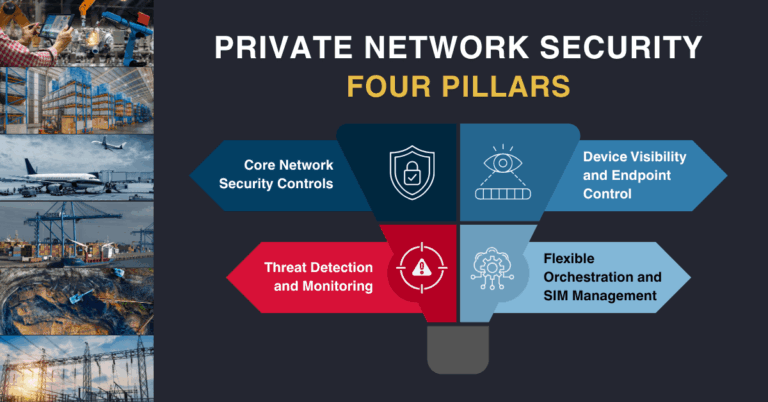
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has started a procedure to identify the 5G spectrum bands, especially those with less commercial prospects for mobile operators that can be distributed through administrative means to businesses to establish and operate captive private networks.
After the department identifies the spectrum for private networks, it will urge the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (Trai) to determine pricing through administrative allocation. A senior official indicated that Trai had already selected some airwaves suitable for such networks; however, DoT wants further to identify additional frequencies with a lessened financial potential.
According to a government official, the plan is not to reserve spectrum for captive networks that have high demand and require an auction. Trai has proposed that at least 40 MHz slices be allocated within the 3700-3800 Mhz and 4800-4990 Mhz bands to put aside for exclusive private networks. Furthermore, Trai encouraged that a minimum of 400MHz in the 28.5-29.5GHz band should be set apart from both satellite earth stations and private networks alike.
The majority of businesses that are in the process of obtaining dedicated spectrum access for individual networks have requested airwaves through the bands officially identified by Trai. Recently, the immensely sought-after 3700-3800 MHz or mid-band spectrum was auctioned off for 5G services. Moreover, 3300-3670 MHz spectrum also went on sale in this particular auction. According to industry sources, companies such as Infosys, Capgemini, GMR, L&T, Tata Communications, Tata Power, and Tejas Networks have all applied to the DoT for spectrum allocation in select regions within that band.
In addition to the mid-band, companies have looked for spectrum in the 28.5-29.5 GHz and 4800-4990 MHz (or millimeter wave) bands as well.
DoT has received a total of 18 applications in response to its exercise that gauged the demand for spectrum from private corporations. Interestingly, there were multiple requests originating from the same group’s companies.
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) believes that if private networks are to be granted access to spectrum in the mid-band, they should pay a market-determined price due to recent auctions. However, no final decision has been made on this issue, and DoT is awaiting recommendations from the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (Trai).
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has released initial guidelines for private networks that will enable businesses to lease spectrum from telecom operators or acquire it directly from DoT. Additionally, enterprises can even ask telecom providers to install their own individualized networks — which is the case with Airtel’s recent agreement with Tech Mahindra to deploy a captive network at Mahindra’s Chakan facility.
The Department of Telecommunications has yet to provide a timeline for the direct allocation of spectrum, leaving many industry professionals wondering how long it may take for the government to publish relevant regulations. Estimates range from one to two years before any definitive rules are released.
Private networks are quickly becoming a game-changer for corporate organizations, who now have the option to set up their own Wi-Fi and data network instead of relying on telecom service providers. Enterprises all over the world recognize that private 5G networks offer enormous potential in terms of capabilities, security, and cost savings – making them an attractive alternative to traditional public network offerings.
Contention has arisen between technology firms and telecom operators over the allocation of spectrum for enterprises to establish their own dedicated 5G networks.
Since the cabinet’s June agreement to offer direct spectrum allocation to businesses, telcos have been in dissent, claiming it would create unfair competition and provide technology companies with a backdoor entry into providing 5G services for enterprises.
Technology firms have asked the government for a direct allotment of 5G spectrum for their private networks, sidestepping telecoms entirely.