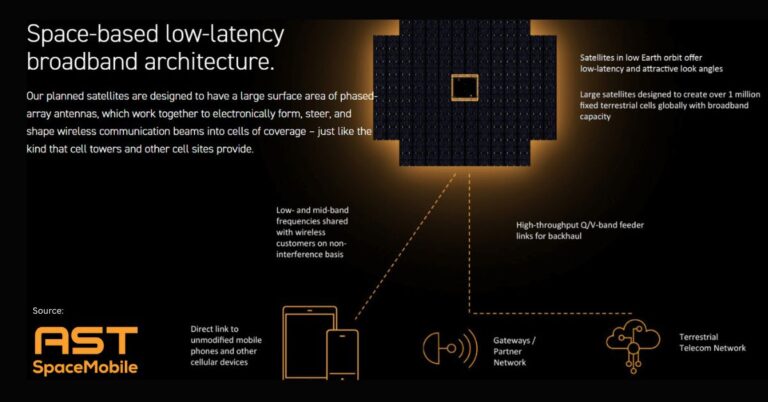
AST SpaceMobile targets intermittent national service in early 2026
AST SpaceMobile is signaling a pivotal year ahead as it moves from demonstrations to commercial direct-to-device coverage with major operators and an aggressive launch schedule.
Market shift from demos to commercial D2D
Direct-to-device connectivity from low Earth orbit is shifting from proofs of concept to real services, and the competitive bar is rising. AST SpaceMobile now has definitive commercial agreements with large carriers including AT&T, Verizon, and stc, plus framework deals with dozens more operators representing nearly 3 billion subscribers. That footprint, combined with over $1 billion in contracted revenue and deep liquidity, puts AST in the first cohort of players attempting national-scale service that reaches ordinary smartphones without special hardware.
The company’s plan to begin “intermittent nationwide” service in early 2026, followed by continuous coverage later in the year, is also a forcing function for device vendors, standards work, and MNO network integration. With T-Mobile US already offering Starlink-based satellite messaging and basic service, the U.S. market is moving quickly; AT&T and Verizon must close the gap with credible timelines and user experiences that go beyond emergency messaging.
Intermittent coverage explained
Intermittent coverage is a function of orbital density and pass timing. With a partial constellation, devices see service in scheduled windows as satellites cross overhead, enabling voice, messaging, and bursts of data. As AST scales to 45–60 BlueBird satellites by end-2026, pass frequency and overlap increase to support “continuous” service across the U.S., Europe, Japan, and other priority markets. The longer-term target of about 90 satellites is intended to broaden global availability and improve capacity.
3GPP NTN, devices, and RAN/core changes
AST’s approach uses LTE and 5G waveforms to talk to unmodified smartphones over partner spectrum, aligning with the broader non-terrestrial network work in 3GPP. The practical lift lives in radio scheduling for high Doppler, timing advance, and power management on the device, plus RAN and core adaptations for satellite access. MNOs should plan for policy control, roaming/billing treatments for NTN, and location accuracy and emergency calling considerations as intermittent moves to continuous service.
Launch cadence, manufacturing scale, and funding
The company has paired a detailed launch cadence with manufacturing scale and a strengthened balance sheet to de-risk the 2026 milestones.
Satellite build-out and launch schedule
AST has five launches planned through the first quarter of 2026, starting with a mid-December mission from India and four additional launches from Cape Canaveral using SpaceX and Blue Origin. New Glenn can carry up to eight BlueBird satellites per flight, while Falcon 9 can carry up to three, enabling a stepwise build to 45–60 satellites by year-end 2026. After Q1, AST expects launches every one to two months to keep pace with coverage and capacity goals.
Satellite manufacturing scale-up
The company expects to reach six satellites per month from December, with 19 built to date and approximately 40 targeted by the end of March. These large, high-gain LEO platforms are designed to close the link budget with standard smartphones on licensed spectrum, which is central to the business case: no user terminals, and distribution through existing MNO channels.
Contracts, revenue, and cash position
AST reports over $3.2 billion in cash and liquidity, plus rising near-term revenue from gateways and U.S. government contracts, though core service revenue awaits network activation. The company’s 1,800-person workforce is shifting from R&D to operations, with a focus on launch execution, ground segment scaling, and operator integrations for early markets including the U.S. and Canada.
D2D competitors and operator partnerships
The U.S. D2D race now features differentiated partnerships, service definitions, and rollout speeds that buyers should evaluate carefully.
AT&T/Verizon partnerships and trials
AST has positioned itself as the satellite RAN extension for AT&T and Verizon, leveraging their licensed spectrum and subscriber bases. Recent demonstrations in Canada with Verizon and Bell highlight VoLTE calls, live video, and broadband data from space to unmodified smartphones. If service quality meets expectations, these partnerships give AST fast lanes into postpaid bases and rural footprints where coverage extension has strategic and regulatory relevance.
T-Mobile/Starlink early lead
T-Mobile, working with Starlink, began offering satellite-enabled service this year, giving it a time-to-market advantage. However, the service mix, device compatibility, and throughput experiences will evolve for both camps as networks densify. The race will likely hinge on practical KPIs—successful call setup rates, latency for voice, uplink reliability, and usable downlink for messaging, emergency services, and basic apps—rather than headline speeds.
Roaming footprint and multinational service
AST’s portfolio of more than 50 operator agreements suggests a path to multinational service and consistent pricing models, which will matter for cross-border logistics, maritime, and aviation use cases. Buyers should scrutinize partner coverage maps, traffic steering policies, and how intermittent service is communicated to end users.
Key NTN risks: spectrum, capacity, integration
As with any first-of-kind network, execution risks span spectrum, interference, capacity, and regulatory compliance.
Spectrum sharing and interference safeguards
Using terrestrial licensed spectrum from space requires tight coordination to avoid interference with macro and small cells. Expect conservative initial footprints, power control constraints, and geofencing until coexistence is proven at scale. Public documentation on spectrum use and protection criteria will be key for regulators and adjacent operators.
Capacity limits and QoS expectations
Per-beam capacity on D2D links will be limited versus terrestrial LTE/5G. Early offers should be framed around essential connectivity: voice, messaging, and moderate data. Latency will be higher than terrestrial but workable for voice if managed; enterprise customers should test critical apps and telemetry under intermittent and continuous modes.
Gateway backhaul and core integration
Backhaul to gateways, policy control in the core, lawful intercept, emergency calling, and location services all require careful integration. MNOs should validate handover behaviors between terrestrial and satellite layers, charging records for satellite sessions, and customer support workflows tailored to pass-based connectivity.
Buyer playbook for NTN/D2D adoption
With 2026 approaching, procurement, engineering, and product teams should prepare staged adoption plans tied to clear KPIs.
MNO/MVNO integration roadmap
Finalize NTN integration roadmaps covering spectrum coordination, device acceptance, emergency services, and billing. Pilot in rural and disaster-prone areas first, with defined SLAs for voice setup success, MOS for VoLTE, message delivery times, and data session reliability. Align marketing to “essential connectivity” and publish transparent coverage windows during the intermittent phase.
Enterprise and public sector use cases
Identify use cases that benefit most from resilience over raw throughput: field safety, grid monitoring, rail and highway operations, maritime, and public safety. Run field trials with the specific smartphones and apps your workforce uses. Require terms that address priority access during incidents, integration with MDM/UEM, and data sovereignty at gateways.
Procurement checklist for D2D/NTN
Ask vendors for constellation timelines by market, device support lists, expected pass frequency during intermittent service, service tiers and fair use policies, emergency services compliance, and incident response procedures. For multinational deployments, confirm roaming coverage, pricing harmonization, and support SLAs across partners.
Bottom line: AST SpaceMobile’s 2026 roadmap, if executed, will turn satellite-to-phone from a niche into a network layer. The winners will be those who productize around realistic performance, integrate cleanly with MNO cores, and deliver simple experiences when users need them most.