CNES picks Capgemini and Thales for 5G NTN D2D demo
France’s space agency CNES has selected Capgemini, Thales, and Thales Alenia Space to lead a national demonstration of 5G direct-to-device (D2D) satellite connectivity under the France 2030 investment program.
Consortium roles and France 2030 backing
The consortium will deliver “U DESERVE 5G,” a government-backed project designed to prove that standard mobile devices and fixed terminals can connect directly to a satellite using 5G non-terrestrial network (NTN) technology. Thales Alenia Space will lead the space segment and payload integration, Thales will contribute secure communications and system engineering, and Capgemini will focus on end-to-end integration, software, test environments, and user experience validation. CNES funding and technical oversight signal France’s intention to accelerate sovereign capabilities in satellite-to-cell, complementing national coverage and crisis-resilience goals.
LEO payload, active beamforming and regenerative 5G NTN
The team will launch a low Earth orbit (LEO) demonstrator satellite equipped with an active antenna payload able to form and steer beams directly to devices. The architecture aims to enable voice and data sessions from a handset to the satellite without an intermediary ground relay, implying a regenerative payload approach that embeds 5G functions onboard. The trial will exercise the full stack—space payload, NTN ground segment, and test devices—across multiple scenarios to evaluate interoperability with terrestrial 5G, handover behavior between networks, and user experience under varying coverage conditions.
Why 3GPP-aligned D2D matters for 5G coverage
The project advances 3GPP-aligned satellite-to-cell at a time when MNOs and enterprises are seeking resilient, ubiquitous connectivity without bespoke hardware.
3GPP NTN roadmap and global D2D competition
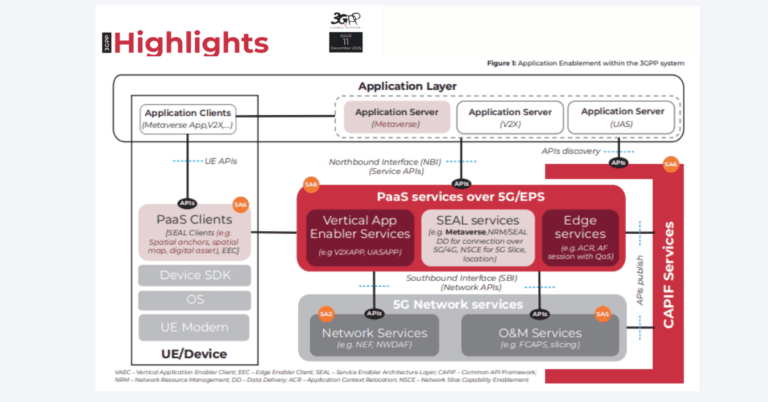
3GPP Release 17 established NTN support for 5G and IoT, and Release 18 is expanding performance and mobility features needed for higher-throughput services and better device integration. Global players—from AST SpaceMobile and Lynk Global to Starlink’s direct-to-cell initiatives with mobile operators—are racing to commercialize satellite-to-smartphone services. This French effort positions European vendors and integrators with a standards-based alternative that can mesh with operator cores and spectrum policies, while aligning with broader European ambitions for secure, sovereign space connectivity. For Thales Alenia Space, the program builds on years of contributions to 5G-by-satellite standardization, and for Capgemini and Thales, it extends their roles in 5G, cybersecurity, and mission-critical networks into NTN.
Benefits for operators and enterprises from satellite-to-cell
Standard-based D2D creates a path to supplement terrestrial 5G with coverage continuity over rural areas, maritime and air corridors, and during disasters. If interoperability and mobility work as designed, operators can offer seamless service without requiring satellite-specific devices, simplifying roaming, billing, emergency calling, and QoS policy. Enterprises in energy, transport, public safety, and logistics gain a new option for primary or backup connectivity where fiber and macro coverage are unreliable, potentially reducing the need for separate satellite terminals and proprietary protocols.
Key 5G NTN challenges to commercialize D2D
The demonstration will address multiple engineering hurdles that determine commercial viability and service quality.
Terrestrial–NTN handover and mobility
Seamless switching between terrestrial and non-terrestrial links is non-trivial given different link budgets, timing advance, HARQ behavior, and beam management. LEO orbits add Doppler and fast-changing geometry, so the project’s handover scenarios will be critical to prove user-transparent mobility, session continuity, and consistent policy application across networks.
Spectrum, licensing and compliance hurdles
D2D services must navigate authorization in mobile satellite service (MSS) bands as well as potential supplemental coverage models in cellular bands, depending on the jurisdiction. Harmonization with national regulators, lawful intercept, emergency services compliance, and cross-border coordination will shape deployment models and roaming agreements. France’s involvement through CNES can streamline local regulatory engagements and influence European harmonization discussions.
Handset, chipset and power readiness
Commercial scale depends on broad handset and module support for NTN features introduced in 3GPP, including waveform adaptations, power control, timing, and GNSS-assisted operations. The trial’s use of test devices will inform requirements for OEM SKUs, RF front-end design in L/S bands, and power management. Integration with modern 5G modems and eSIM/eUICC profiles will be a gating factor for mass-market services.
Action plan for operators, enterprises and vendors
Operators and enterprises can use this initiative as a catalyst to build practical roadmaps for satellite-to-cell augmentation.
Operator steps: lab validation, core integration, spectrum
– Launch lab evaluations with NTN-ready chipsets and simulate Doppler, delay, and beam dynamics to validate RAN and core behavior.
– Define service models: supplemental coverage for messaging and voice, or differentiated tiers for broadband, with clear SLAs and pricing.
– Plan core integration and policy alignment (authentication, roaming, charging, emergency services, lawful intercept) with satellite partners.
– Engage regulators early on spectrum use, especially for MSS bands and any hybrid licensing models.
Enterprise playbook: use cases and resilience
– Map mission-critical use cases—field ops, remote assets, maritime, rail, emergency response—to D2D coverage and throughput profiles.
– Pilot multi-path WAN designs that bond terrestrial 5G with NTN for continuity and resilience, including zero-trust overlays.
– Update device and fleet procurement criteria to include NTN-capable modules and eSIM policies.
Vendor roadmap: 3GPP NTN features and APIs
– Align product roadmaps with 3GPP Release 17/18 NTN features and publish reference architectures for satellite-integrated 5G cores and RAN.
– Contribute to interoperability testing, open APIs for policy/charging, and observability across terrestrial and NTN domains.
Next steps: in-orbit demo and commercialization
The demonstration will move from payload integration and ground testing to in-orbit trials, producing data that will shape commercial offerings and partnerships.
Milestones: payload, ground readiness, phased trials
Key milestones include payload validation, ground segment readiness, and phased service trials to measure call setup, data throughput, mobility, and energy consumption at the device. Results will inform spectrum strategies, roaming constructs, and the business case for nationwide or pan-European expansion.
Success metrics: mobility, QoS and core integration
Watch for evidence of standards-compliant mobility between terrestrial and NTN, stable voice and data sessions on unmodified or lightly modified devices, acceptable latency and error rates for target use cases, and operator-friendly integration with core networks and OSS/BSS systems.
Bottom line: CNES’s backing of Capgemini, Thales, and Thales Alenia Space gives France a credible, standards-based path to satellite-to-cell, and the outcome will influence how European operators add NTN to their 5G roadmaps for coverage, resilience, and new revenue.