The U.S. 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) market continues its upward trend as major operators push past subscriber milestones and maintain solid network performance. According to the latest research from Ookla, both T-Mobile and Verizon are expanding their FWA footprint, driven by increasing consumer demand and surprisingly strong download speeds.
5G FWA Adoption Tops 11.5 Million in the U.S.
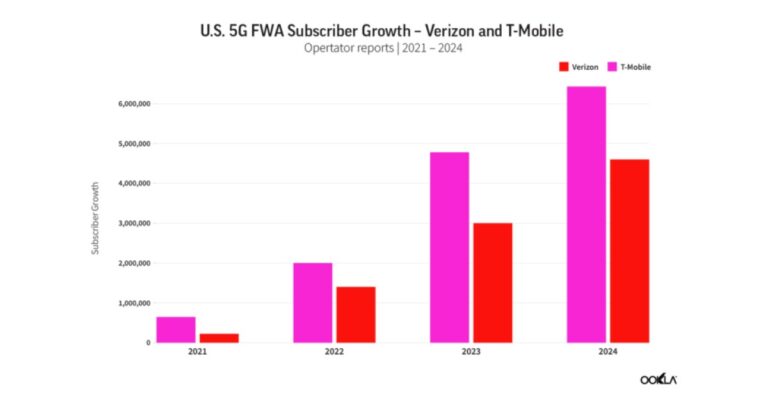
As of Q4 2024, the U.S. has over 11.5 million FWA subscribers across the top three operators: T-Mobile, Verizon, and AT&T. T-Mobile leads with 6.43 million subscribers, followed by Verizon with over 4.3 million, while AT&T, a more recent entrant, has attracted 650,000 customers since launching its Internet Air service in August 2023.
What stands out is the rapid growth in users without a decline in performance. In fact, the opposite has happened.
5G FWA Download Speeds Surge for T-Mobile, Verizon, and AT&T
FWA subscribers are benefiting from faster speeds, as confirmed by Ookla® Speedtest® data. T-Mobile saw its median download speed jump over 50%, from 134.99 Mbps in Q4 2023 to 205.44 Mbps in Q4 2024. Verizon’s median speeds increased by 12%, rising from 132.55 Mbps to 150.47 Mbps. AT&T also improved, going from 126.41 Mbps to 145.30 Mbps in the same period.
T-Mobile execs attribute this improvement to smart network management and a focus on sectors with excess spectrum capacity. During the company’s Capital Markets Day, they highlighted that customers now experience 3x faster speeds compared to when the service launched in early 2021.
Verizon Introduces Speed Caps to Optimize FWA Network Performance
While T-Mobile emphasizes smart spectrum allocation, Verizon takes a more traditional approach to managing network load—speed caps. Verizon’s pricing tiers reflect these limits:
- 5G Home Plus (mmWave/Ultra Wideband): Up to 1 Gbps, $55/month
- Mid-tier 5G Home Plus (Ultra Wideband only): Up to 300 Mbps
- Basic 5G Home: Also capped at 300 Mbps, $35/month
Analysis of the 90th percentile of Speedtest users confirms that Verizon is actively capping speeds just above 300 Mbps.
In contrast, T-Mobile doesn’t enforce strict caps, but it does use data prioritization. Starting January 2024, it implemented a soft usage threshold of 1.2 TB per month. Users exceeding this may see reduced speeds during network congestion.
Upload Speed Trends Highlight T-Mobile’s Lead in FWA Performance
Upload speeds are critical for remote work and video collaboration. Here’s how the carriers performed:
- T-Mobile: Up 9.05%, from 19.88 Mbps to 21.68 Mbps
- Verizon: Up 7%, from 12.84 Mbps to 13.88 Mbps
- AT&T: Down 18%, from 16.62 Mbps to 13.57 Mbps
T-Mobile continues to outperform competitors in this metric, maintaining its edge in both download and upload performance.
T-Mobile Lowers Latency for Improved Real-Time 5G FWA Performance
Latency, a key factor for real-time apps like video conferencing and online gaming, remained mostly flat for Verizon and AT&T but improved for T-Mobile:
- T-Mobile: Down from 61 ms to 52 ms
- Verizon: Slight increase from 52 ms to 53 ms
- AT&T: Minimal improvement from 74 ms to 73 ms
T-Mobile’s lower latency further strengthens its appeal to home broadband users relying on responsive internet connections.
Verizon and T-Mobile Raise 2028 FWA Subscriber Goals
Both Verizon and T-Mobile have upped their FWA subscriber targets for 2028:
- Verizon: From 4–5 million to 8–9 million
- T-Mobile: From 7–8 million to 12 million
T-Mobile plans to stick to its strategy of targeting areas with underutilized 5G spectrum—especially in rural zones—where mobile demand is lower.
AT&T, on the other hand, views FWA as a temporary solution, primarily serving customers with limited broadband options. Its longer-term strategy is to transition FWA users to fiber as coverage expands.
FWA Gains Consumer Preference Over Cable and Fiber in U.S.
Consumer research backs up the momentum behind FWA. A Recon Analytics survey of 288,490 U.S. residents found:
- 44% would choose an FWA provider for their next broadband connection
- 25% preferred fiber
- 17% leaned toward cable
- The rest would opt for DSL or satellite
A separate JD Power report (April 2024) indicated that 5G FWA providers received the highest satisfaction scores among broadband providers, with fiber in second place.
Still, not all FWA users have an ideal experience. Ookla data shows that 10th percentile users—typically during peak hours—see slower speeds. At 8 p.m., the most congested time:
- T-Mobile: 13.50 Mbps
- Verizon: 15.81 Mbps
- AT&T: 15.99 Mbps
This suggests that while FWA performs well for the majority, some users are affected by high-traffic periods.
Regional ISPs Join FWA Market as Competition Intensifies
Beyond the big three, regional and independent players are entering the FWA space. USCellular reported 150,000 FWA customers by the end of 2024. C Spire launched FWA in Mississippi, and BrightSpeed plans to offer a service in partnership with Verizon.
Verizon is also trialing an FWA solution using mmWave for multi-dwelling units (MDUs), aiming for 1 Gbps speeds. A commercial launch is expected soon.
Future of U.S. FWA: Performance, Subscriber Growth, and Market Shifts
With growing FWA subscriber bases and performance improvements, U.S. operators are clearly betting big on this technology. Speedtest data from Ookla shows that 5G FWA is no longer a fallback—it’s becoming a mainstream broadband choice.
Whether it’s Verizon’s high-speed tiers, T-Mobile’s latency improvements, or AT&T’s strategic use of FWA as a transitional service, the fixed wireless landscape is evolving quickly.
As network management techniques mature and 5G infrastructure expands, it will be critical to watch how performance metrics hold up—especially as millions more subscribers come online.
Report Source: This article is based on data and insights from Ookla Speedtest Intelligence®. Analyst Kerry Baker contributed to the original research.