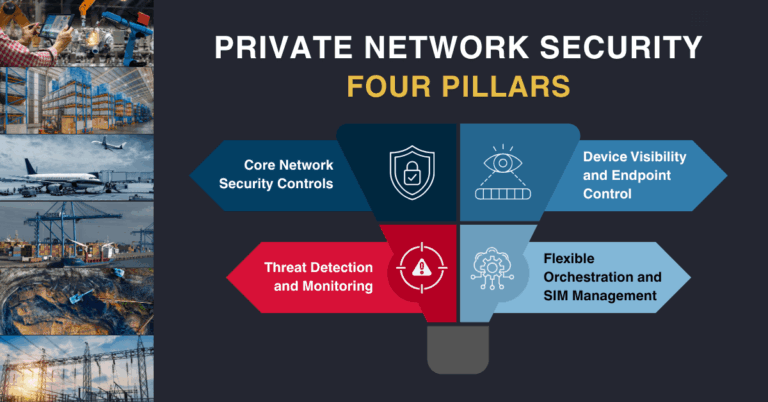
Partnership overview
Tidal Wave Technologies has selected UK-based RANsemi to supply AI-enhanced Open RAN small cells for next-generation industrial private 5G networks across India.
Deployment announcement
The companies will integrate RANsemi’s small cell platform into private 5G systems targeted at harsh, safety-critical environments. Initial focus areas include open-cast coal mines, large port terminals, and complex logistics hubs. The goal is to deliver resilient, low-latency connectivity for automation, remote operations, and worker safety. The partnership will be showcased at India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2025 with a live demonstration of integrated small cells and edge intelligence.
About Tidal Wave and RANsemi
Tidal Wave is an Indian systems integrator for private cellular, with deployments in mining and industrial sites. RANsemi is a wireless semiconductor and platform provider focused on integrated small cells and AI-for-the-RAN. Both companies emphasize edge-deployed intelligence that adapts to dynamic radio conditions in real time.
Why it matters for industrial private 5G
Industrial digitalization in India is accelerating and needs carrier-grade wireless that can operate reliably in extreme conditions.
Industrial 5G: from pilots to scale
Enterprises in mining, ports, and manufacturing are moving beyond pilots to multi-site rollouts. Private 5G supports computer vision, autonomous haulage, remote drilling, crane automation, and predictive maintenance. These use cases demand deterministic performance that Wi‑Fi struggles to guarantee at scale in outdoor, obstructed, or high-interference environments.
Open RAN with AI at the edge
Open RAN and integrated small cells can shrink footprint, improve total cost of ownership, and speed time to deploy. Adding AI at the radio edge enables on-the-fly optimization, anomaly detection, and self-healing—critical when terrain, weather, and interference patterns shift hourly. This aligns with industry momentum toward 3GPP Release 16+ features and O-RAN Alliance interfaces designed for more programmable RANs.
Technology building blocks
The collaboration combines compact radios, on-prem compute, and software that brings intelligence closer to the device and application.
AI-enhanced small cells and edge intelligence
RANsemi’s platform embeds AI/ML to improve scheduling, interference mitigation, and resource allocation. In industrial zones, that can translate to steadier throughput and lower jitter for mission-critical traffic. Real-time insights at the cell site reduce dependence on backhaul and central analytics, improving resiliency when links degrade.
Open RAN integration and optionality
Open RAN-aligned architectures create optionality for transport, core, and OSS selections. Standardized interfaces from the O-RAN Alliance enable multi-vendor integration and future use of RIC applications for closed-loop control. For buyers, this can lower lock-in risk and ease lifecycle evolution as device fleets and applications expand.
Low latency, resiliency, and safety
Industrial private 5G favors on-premises user plane and edge applications to keep round-trip latency low. Designs prioritize redundancy, graceful degradation, and rapid failover. In safety-critical workflows, network behavior must be predictable under load, during handovers, and amid RF obstructions from heavy machinery and terrain.
Early proof points in India
Tidal Wave cites private 5G deployments for Coal India as evidence that the stack can perform at scale in harsh environments.
Coal mining outcomes and lessons
Deployments have supported remote operations, real-time analytics, and improved worker safety across multiple sites. These projects validate coverage planning in open-cast pits, mobility under dust and vibration, and integration with operational technology systems.
Next: ports and logistics
Port terminals require pervasive coverage across yards, cranes, and vessels, with service continuity between indoor warehouses and outdoor berths. Private 5G can simplify spectrum management, secure traffic separation, and QoS for automated guided vehicles, cameras, and RTGs versus manual operations.
Market and ecosystem impact
The deal underscores growing confidence in industrial private 5G and signals maturing vendor stacks tailored to India.
Vendor landscape and alliances to watch
Specialist small cell vendors partnering with regional integrators is a pattern to watch. It complements operator-led private 5G and helps address brownfield industrial integration. Expect more collaborations combining radio, core, MEC, and application ISVs into validated blueprints.
Spectrum and deployment models in India
In India, enterprises typically deploy captive non-public networks in partnership with licensed operators or via approved spectrum arrangements. Buyers should align architecture choices—standalone core, on-prem UPF, and slicing options—with local regulatory frameworks and site constraints.
Device and application ecosystem needs
Success hinges on ruggedized 5G devices, certified industrial gateways, and application partners for video analytics, asset tracking, and control systems. 3GPP Release 16+ capabilities, such as enhanced URLLC features and time-sensitive networking integration, are relevant but depend on end-to-end support across radios, devices, and applications.
Key challenges
Industrial private 5G succeeds when RF realities, OT integration, and operational risk are addressed early.
RF propagation and hardening
Mines and ports present NLOS paths, moving obstructions, and harsh climates. Designs must account for antenna placement, backhaul diversity, and environmental hardening, plus safe maintenance access for small cells.
OT integration and cybersecurity
Tight coupling with SCADA/PLC systems requires deterministic behavior, role-based isolation, and rigorous change control. Security baselines should include zero-trust principles, device attestation, and continuous monitoring tailored to critical infrastructure.
AI governance and lifecycle management
AI in the RAN introduces data governance, model drift, and explainability considerations. Enterprises need MLOps processes, rollback plans, and KPIs that link model outcomes to service-level objectives for safety and availability.
Next steps for enterprises
Procurement and engineering teams should translate ambition into measurable, site-specific requirements and pilots.
Define use cases and KPIs
Prioritize two to three high-value workflows and set KPIs for latency, reliability, coverage, and video quality. Include safety and productivity metrics, not just RF indicators.
Architect for resilience and redundancy
Specify on-prem edge, UPF placement, and redundancy targets. Validate handovers, interference management, and failover under realistic load and mobility.
Select partners and plan operations
Assess Open RAN maturity, integration accountability, and multi-year support. Build spares, training, and change-management into budgets. Require documented security and AI lifecycle practices.
What to watch at IMC 2025
The joint demonstration will be a litmus test for readiness and real-world operability.
Signals of maturity to track
Look for performance under mobility, mixed traffic profiles, and environmental emulation. Evidence of closed-loop optimization, rapid recovery, and simplified operations will matter more than peak throughput.
Ecosystem breadth and support
Note which device types, cores, and application partners are supported. The wider the validated stack, the lower the integration risk for multi-site rollouts in 2025–2026.