Lumen AI Backbone Expansion: Scope and Strategy
Lumen is accelerating a multi-year, multi-billion-dollar expansion of its U.S. backbone to match the explosive rise of AI-driven traffic.
34M New Intercity Fiber Miles and Coast-to-Coast Routes
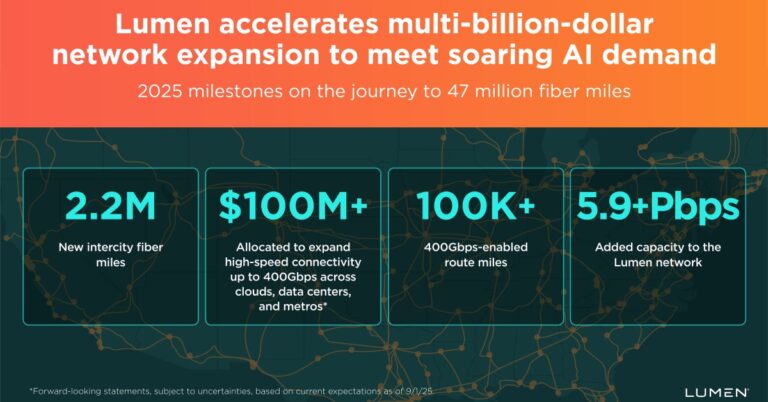
The company plans to add 34 million new intercity fiber miles by the end of 2028, targeting a total of 47 million intercity fiber miles. Executives frame the effort as more than incremental—aiming to more than double the size of Lumen’s U.S. network footprint to serve AI training, inference, and data movement at scale. The build spans coast-to-coast routes with an emphasis on ultra-low-loss fiber, route diversity, and tighter integration with metro, data center, and cloud on-ramps.
2025 Build Milestones: 400G Rollout, Capacity Adds, IRU Conduits
In 2025, Lumen has already added more than 2.2 million intercity fiber miles across 2,500+ route miles, with a year-end target of 16.6 million intercity fiber miles. Construction is underway at 176 In-Line Amplifier sites, with next-generation shelters designed for higher power density and future capacity upgrades. The company completed IRU conduit deployments across 55 routes, expanding control over underground pathways to speed later fiber additions. Network capacity grew by 5.9+ Pbps year-to-date, and Lumen earmarked more than $100 million to push 400Gbps connectivity across clouds, data centers, and metros—now covering over 100,000 route miles with 400G-enabled transport.
Why the Build Matters for AI Training and Inference
AI is changing traffic patterns and performance targets, and the backbone must keep pace with east–west data flows, GPU cluster interconnects, and edge latency needs.
East–West Data Movement and Private Connectivity Fabric (PCF)
Model training, retrieval-augmented generation, and multi-cloud architectures are driving sustained east–west data movement between core data centers, peering sites, and edge locations. Public internet paths rarely meet the predictability or security thresholds for high-value AI workloads. Lumen’s Private Connectivity Fabric (PCF) is positioned to offer deterministic, privately routed capacity across cities and regions, with fiber engineered for lower optical loss and higher spectral efficiency. For enterprises, that means more headroom to scale DCI and interconnect AI pipelines without constant re-architecting of routes and SLAs.
Latency Targets, Optical Loss, and 400G Readiness
Lumen highlights sub-5-millisecond edge latency coverage for up to 97% of U.S. business demand and route diversity across 50+ major cities. Lower optical loss enables longer spans and fewer regenerations, reducing points of failure and operating costs. Expanding 400G across cloud on-ramps and metro cores shortens provisioning cycles and simplifies scaling for AI data transfers. As operators broadly adopt coherent optics, C+L band capacity, and automated wavelength provisioning, enterprises benefit through faster turn-ups and more predictable performance for GPU-to-GPU traffic.
Fiber, Amplification, and Vendor Partnerships
The build leans on fiber innovation, modern amplification, and conduit control to increase capacity density and deployment velocity.
Next-Gen Fiber, ILA Sites, and Capacity Engineering
Lumen is deploying next-generation fiber optic cable from Corning Incorporated to place roughly twice as many fibers in existing conduits, which is critical as rights-of-way become scarce and metro congestion grows. The company reports using fiber with about 25% less optical loss than older vintages, coupled with designs they say deliver around 60% more capacity than traditional builds. New ILA sites are architected for higher power density and easier upgrades, enabling more coherent wavelengths and spectrum per route as demand ramps.
Conduit IRUs and Route Diversity for Resilience
Completing IRU conduit deals across 55 additional routes signals a long-term bet on physical path control. Conduit IRUs de-risk future builds by shortening construction cycles and allowing rapid fiber pulls when capacity is needed. Combined with diverse long-haul paths and metro off-ramps, this approach improves resiliency for AI workloads that must avoid correlated failures affecting multiple regions or cloud zones.
Market Context and Competitor Comparison
The move lands amid a national arms race to connect data centers, clouds, and edge zones with higher-capacity, lower-latency transport.
Comparing National Backbones: Performance and Coverage
Carriers and fiber operators across North America are expanding long-haul routes, lighting dark fiber, and upgrading to 400G and beyond to meet hyperscaler and enterprise demand. Lumen’s claim of operating the largest ultra-low-loss intercity fiber network in North America signals a strategy to differentiate on optical performance and breadth of coverage. For buyers evaluating providers for AI DCI and inter-region transport, factors like loss budgets, route diversity, automation APIs, and time-to-capacity are becoming as important as raw bandwidth price.
Alignment with Hyperscaler and Data Center Expansion
Hyperscalers are concentrating on new campuses in Virginia, Ohio, Texas, Arizona, and the Midwest, with rapid growth in GPU clusters and power-hungry AI halls. The economics of private optical fabrics improve as enterprises split workloads across AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and specialized AI clouds. Lumen’s investment to extend 400G to cloud nodes and key metros aligns with that multi-cloud reality, providing deterministic paths for training data ingress, model distribution, and high-volume inference backhaul.
Execution Risks, Constraints, and Watchlist
Execution will hinge on capital discipline, construction throughput, and energy availability along critical routes.
Capital, Construction, and Power Constraints
Fiber builds face permitting delays, construction risk, and supply dynamics for cable, amplifiers, and electronics. Power constraints around new ILA sites and data center clusters can slow timelines. Watch for updates on route turn-ups, utilization of the 400G footprint, and how quickly Lumen converts IRU conduit into lit capacity. Performance of latency and availability SLAs will be key leading indicators for AI buyers.
Standards, Open APIs, and Interoperability
Enterprises should track alignment with MEF service definitions for on-demand connectivity, adoption of open APIs for automation, and compatibility with coherent pluggable ecosystems such as 400ZR/ZR+. Interoperability across cloud on-ramps and carrier-neutral facilities matters when stitching multi-region AI pipelines and ensuring consistent telemetry and observability.
Enterprise Actions and Planning Guidance
Network leaders should align AI roadmaps with transport strategies that assume sustained east–west growth and stricter latency envelopes.
Near-Term Network Actions
Audit inter-region paths, jitter, and loss budgets for AI data flows; right-size to 100G/400G where needed. Prioritize private connectivity to cloud and data centers for predictable performance. Engage providers on route diversity and failover design, including separation from major internet corridors. Explore wavelength services versus dark fiber based on control, agility, and operating model.
Strategic Planning for 2026–2028
Map AI workload placement to backbone evolution, including emerging edge zones. Negotiate SLAs tied to latency, availability, and provisioning intervals, with visibility into optical telemetry. Evaluate providers’ conduit positions, ILA roadmap, and fiber characteristics—not just price per Gbps. Plan for automation via APIs to align provisioning speed with AI cluster scaling, and pressure-test multi-cloud paths for future 800G and higher capacity waves.