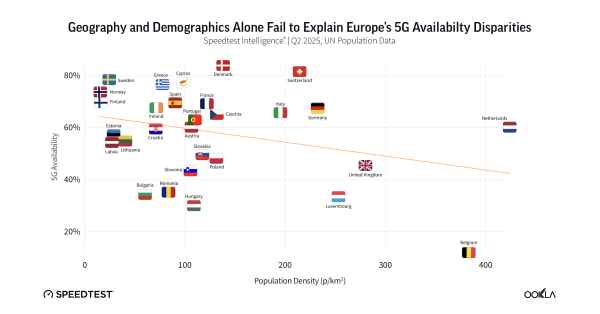
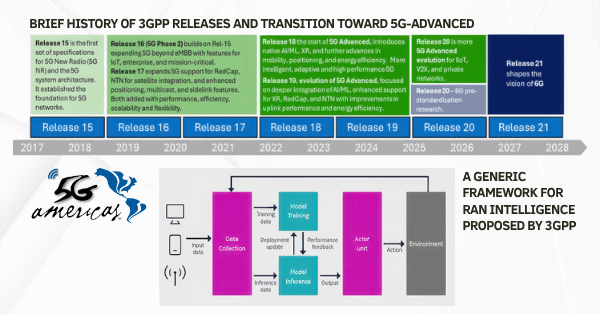
Since its launch, 5G technology has promised transformative potential across industries and daily life, yet its impact is only gradually taking shape. Five years in, 5G is showing real benefits in specific industrial applications, while broader consumer uses are still evolving. Here’s an in-depth examination of 5G’s journey, its impact, and what’s next for this transformative technology.
5G’s Initial Promise vs. Current Reality
The arrival of 5G in 2019 stirred up excitement across the telecom and tech sectors. Providers touted 5G as the technology that would redefine connectivity, supporting applications like ultra-fast mobile internet, virtual reality (VR), and smart cities. Initial expectations centered around speed and the promise of seamless, real-time interactions for consumers and businesses alike. However, while 5G networks are now present in many urban centers, their high-speed, low-latency promise has been constrained by limited infrastructure, especially in regions where deployment relies on modified 4G technology.
As a result, consumer applications that depend on full 5G performance, such as immersive VR or remote-controlled healthcare procedures, are still mostly aspirational. The adoption rate has also been slowed by high costs, limited device compatibility, and infrastructure requirements. Despite this, 5G technology has gained ground in industries that benefit from targeted, high-performance connectivity, paving the way for future growth and innovation.
Industrial Applications of 5G: What’s Working Today
While consumer use of 5G is still growing, industries like mining, manufacturing, and energy are finding ways to leverage 5G’s capabilities to boost efficiency, automation, and safety. Here’s an overview of where 5G is already proving valuable in real-world industrial settings:
| Application | Industry | Impact of 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance | Manufacturing | Allows for real-time monitoring to predict and prevent equipment failures, minimizing downtime |
| Automated Quality Control | Manufacturing | Supports real-time inspection with high-resolution sensors, reducing errors and improving quality |
| Remote Mining Operations | Mining | Enables control of machinery from safe distances, reducing risks in hazardous mining environments |
| Smart Grid Management | Energy | Provides real-time data on grid health and demand, enabling faster responses and enhancing stability |
| Warehouse Robotics and Automation | Logistics | Supports efficient communication among robots, enabling real-time coordination for order processing |
These industrial applications illustrate 5G technology’s impact in enhancing productivity and safety in sectors where connectivity has a direct impact on operations. The cost of implementation remains a barrier for some organizations, but the high return on investment is driving continued adoption within these specific use cases.
Global 5G Rollout: Key Regional Developments and Challenges
The global rollout of 5G has progressed unevenly, with certain regions leading the way and others facing challenges related to infrastructure and investment. According to 5G Americas and TeleGeography’s October 2024 data, here’s a snapshot of 5G’s deployment across regions:
| Region | LTE Networks | 5G Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Africa | 163 | 43 |
| Asia | 138 | 65 |
| Europe | 167 | 117 |
| Latin America | 133 | 49 |
| Middle East | 49 | 26 |
| Oceania | 39 | 16 |
| U.S. & Canada | 18 | 17 |
| Global Total | 707 | 333 |
This regional breakdown highlights disparities in 5G access, particularly in rural or underserved areas where network infrastructure has been slower to expand. In more connected regions, the focus is on optimizing 5G’s performance, while less connected areas emphasize the need for basic infrastructure investments to support 5G technology access.
U.S. 5G Insights: The Role of Mid-Band Spectrum in Nationwide Deployment
In the United States, the 5G technology experience underscores the importance of mid-band spectrum in delivering reliable performance. Major carriers, such as T-Mobile and AT&T, have expanded their 5G networks by acquiring C-band and 3.45 GHz spectrum, essential for enhancing network performance and expanding reach, especially in rural areas. This mid-band spectrum provides a balance of speed and coverage, which is crucial for a consistent 5G experience across urban and rural areas alike.
| Carrier | Spectrum Acquired | Median Download Speed |
|---|---|---|
| T-Mobile | 2.5 GHz | ~287 Mbps |
| Verizon | C-band | ~225 Mbps |
| AT&T | 3.45 GHz | ~145 Mbps |
These spectrum investments have resulted in significant performance improvements. T-Mobile has utilized its 2.5 GHz holdings to achieve some of the highest 5G speeds across the country. Verizon’s C-band deployment (https://www.verizon.com/5g/) has similarly bolstered its network, particularly in urban regions, while AT&T is steadily building out its 3.45 GHz network.
Despite these advancements, disparities in 5G speed and access persist across states. Urban areas in states like Illinois and Minnesota report high speeds due to robust infrastructure, while rural states like Mississippi experience slower speeds. This uneven performance highlights the need for continued investment in mid-band spectrum and infrastructure to bridge the digital divide and create a more equitable 5G landscape across the United States.
For further detailed insights and 5G performance metrics in the U.S., you can explore these reliable sources:
- FCC Spectrum Auctions and Data
- OpenSignal U.S. Mobile Network Experience Reports
- Ookla Speedtest Global Index
- 5G Americas White Papers and Insights
These sources offer comprehensive data on U.S. 5G deployment, spectrum utilization, and performance statistics, underscoring the importance of mid-band spectrum in shaping the national 5G landscape.
Key Takeaways from the First Five Years of 5G Technology
Reflecting on the initial years of 5G provides insights into how future network rollouts, such as 6G, might be better planned. Key takeaways include:
- Targeted Applications Drive Adoption: Industry-specific applications, like predictive maintenance and V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communications, drive faster adoption than speculative consumer applications. Practical uses with clear, immediate benefits lead the way in creating demand.
- Infrastructure Investment: Reliable and widespread 5G access requires significant investment, especially in underserved areas. Without this foundational infrastructure, 5G’s full potential will remain unrealized.
- Cross-Sector Collaboration: Establishing standards and ensuring interoperability requires collaboration among telecom providers, industry stakeholders, and government entities. Collaborative ecosystems are essential for scaling 5G applications.
- Beyond Speed: Prioritizing Reliability: Although 5G’s high-speed connections are appealing, industries value its low latency and reliable connectivity more. Emphasizing these features can help future networks focus on practical applications that enhance safety and productivity.
5G and IoT: Fueling the Future of Connected Applications
5G’s low latency and high bandwidth make it ideal for expanding the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, particularly in sectors that rely on data-heavy, real-time applications. Here’s how 5G is enabling IoT-driven innovation across different industries:
| Sector | IoT Application | 5G’s Role |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Smart irrigation, soil monitoring | Enables remote management, optimizing water and resource usage for efficiency |
| Smart Cities | Traffic control, waste management | Supports data collection and responsive systems for efficient urban services |
| Healthcare | Remote diagnostics, connected devices | Provides continuous, reliable data for real-time patient monitoring |
| Utilities | Energy monitoring, leak detection | Enables predictive maintenance, improving resource management |
| Logistics | Asset tracking, inventory management | Ensures precise tracking and on-time delivery through real-time communication |
5G is essential for scaling IoT networks to support these applications, as it provides the speed and responsiveness required for large-scale data management and automation. This capability positions 5G as a foundation for widespread IoT adoption.
Addressing Cybersecurity Challenges in a 5G-Connected World
As 5G accelerates connectivity, it brings new cybersecurity challenges that require innovative approaches to network security. With more devices connecting through IoT, each networked device adds potential vulnerabilities. Therefore, robust cybersecurity strategies are crucial:
| Security Challenge | Implication | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Expanded Attack Surface | More devices increase entry points for cyber threats | Network segmentation, routine security audits |
| Data Privacy Risks | Sensitive data may be exposed during transmission | End-to-end encryption, secure access protocols |
| IoT Device Vulnerabilities | Many IoT devices lack built-in security | Firmware updates, secure coding for devices |
| Complex Network Security | Diverse devices complicate network management | AI for threat detection and response automation |
Addressing these security challenges is critical to ensuring that 5G’s benefits aren’t overshadowed by data privacy concerns and cyber risks. Strong security frameworks will enable industries to adopt 5G with greater confidence, particularly in data-sensitive applications.
How 5G Technology Supports Global Sustainability Goals
5G can play a significant role in supporting global sustainability objectives by enabling resource-efficient practices and reducing environmental impact. Here’s a look at 5G’s contributions to green goals:
| Sustainability Objective | 5G’s Contribution | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Enables smart grid management, reducing energy waste | Real-time monitoring of energy use and efficient adjustments |
| Emissions Reduction | Supports traffic management to reduce vehicle emissions | V2X communication to optimize traffic flow |
| Water Conservation | Facilitates precision agriculture, optimizing water use | Smart irrigation and soil moisture tracking in agriculture |
| Reduced Industrial Waste | Predictive maintenance to avoid breakdowns and waste | Manufacturing equipment monitoring and predictive repair |
By supporting sustainable practices in agriculture, energy, and transportation, 5G aids in creating more efficient, environmentally friendly operations. This alignment with green goals underscores 5G’s role in not only advancing technology but also contributing to global sustainability.
Impact of 5G Technology on Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs)
Beyond large industries, 5G technology offers small and medium businesses (SMBs) opportunities to modernize operations, improve customer engagement, and compete on a larger scale. Here’s how 5G technology is making an impact on SMBs:
| Business Function | 5G’s Impact | Potential Benefits for SMBs |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Customer Engagement | Improves digital services and mobile app performance | Higher customer satisfaction and loyalty |
| Operational Efficiency | Enables remote work, cloud access, and video conferencing | Cost reduction and increased flexibility |
| Data-Driven Decisions | Real-time data collection for better insights | Faster, more informed decision-making |
| E-commerce and Logistics | Improves speed and reliability of online services | Enhanced customer experience and order accuracy |
| AR for Marketing | Enables immersive product displays for customers | Engaging in-store and online shopping experiences |
For SMBs, 5G can enhance competitiveness by providing access to digital tools and data-driven insights. As the technology becomes more accessible, 5G will help SMBs adopt modern practices to boost efficiency, customer satisfaction, and operational agility.
Beyond 5G Technology: Lessons for Future Network Generations
Looking ahead to the next generation of networks, such as 6G, 5G’s rollout provides important lessons on what to prioritize. Key considerations for future networks include:
| Insight | Lesson for Future Networks | 6G Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Necessity over Novelty | Focus on practical applications that solve real needs | Prioritize essential, high-value use cases |
| Bridging Digital Divides | Expand connectivity in underserved regions | Invest in rural and less connected areas |
| Cross-Sector Collaboration | Encourage partnerships to develop standards and use cases | Build a cooperative ecosystem to foster innovation |
| Built-in Security | Address cybersecurity at the core of network design | Proactively secure networked devices and data flows |
| Sustainability as a Priority | Align with energy-efficient and eco-friendly practices | Reduce carbon footprint of infrastructure and devices |
The next generation of networks will likely emphasize inclusivity, security, and sustainability over speed alone. Learning from 5G, future networks can deliver more targeted, practical advancements that meet the needs of society and industry alike.
Conclusion: 5G Technology’s Gradual but Promising Path
Five years into 5G’s journey, its impact has been slower but more focused, with industrial applications leading the way. The technology’s greatest contributions have emerged in areas like manufacturing, logistics, and energy, setting the foundation for future growth. Moving forward, 5G’s success will rely on infrastructure expansion, practical use cases, and collaboration among sectors to address real-world needs.
Looking ahead, 5G’s legacy will likely be one of targeted, practical impact, particularly in industrial and IoT applications that benefit from high-speed, low-latency connections. By focusing on these strengths, 5G can pave the way for more inclusive and sustainable connectivity, setting a roadmap for future technological advancement grounded in tangible societal and industrial value.