Small cells enter scaled growth as enterprises and neutral hosts lead
The Small Cell Forum’s 2025 Market Forecast points to a market shifting from experimentation to scaled deployment, with enterprise demand and new business models driving a faster cadence.
Forecast: 61M shipments by 2030, 9.4% CAGR
SCF forecasts cumulative small-cell shipments to reach 61 million units by 2030, supporting an installed base of roughly 54.4–54.5 million radio units and annual vendor/integrator revenues of about USD 4.23 billion. The baseline growth rate has been lifted to a 9.4% CAGR through the period, up from 8.6% in last year’s outlook, based on surveys of 96 mobile operators and service providers. Indoor enterprise deployments continue to dominate, representing about 60% of rollouts in 2023–2024 and stabilizing near 54% by 2030 as outdoor densification and public network sharing also scale.
Why now: indoor economics, neutral host, edge, 5G SA
The economics of coverage and capacity are shifting indoors, where most traffic originates and where public macro layers struggle to meet performance and reliability requirements for industrial IoT, automation, and high-capacity venues. At the same time, neutral host models, edge compute integration, and 5G Standalone (SA) are converging to deliver predictable latency, multi-operator reach, and application-aware networks. The result is a denser, more programmable RAN that is better aligned to enterprise workflows—and a broader set of deployers beyond traditional MNOs.
Enterprise indoor and neutral host drive deployment momentum
The strongest near-term momentum lies in multi-tenant indoor systems that translate performance into business outcomes while lowering total cost of ownership.
Enterprise use cases shift from pilots to production
Growth in private and hybrid small-cell networks is anchored in high-value use cases: autonomous robotics and machine vision in factories and logistics, staff safety and asset tracking in healthcare, high-capacity retail and public-sector facilities, and performance-critical back-of-house connectivity in hospitality and stadiums. These sites require deterministic coverage, uplink performance, and tight integration with IT and cybersecurity controls—needs that favor small cells over Wi‑Fi alone and drive demand for 5G SA features such as QoS, slicing, and time-sensitive networking as 3GPP Release 17/18 capabilities mature.
Neutral host share doubles in enterprise by 2030
SCF projects the share of enterprise small cells deployed and operated by neutral hosts to double from 14% to 28% by 2030, making it the fastest-growing commercial model. In public networks, neutral host is also rising, reaching an estimated 27% of new deployments by 2030, up from 8% in 2023. The attraction is clear: multi-operator coverage via MOCN/MORAN, lower capex for MNOs, and faster time-to-service for landlords. Neutral host specialists and towercos—players such as Boldyn Networks, Cellnex, Crown Castle, American Tower and Dense Air—are standardizing multi-operator blueprints and service-level constructs to reduce engineering friction across venues and markets.
What this means for MNOs and enterprises
For MNOs, neutral host can achieve indoor coverage obligations and enterprise reach without one-off builds, while preserving control via shared cores and APIs. For enterprises, neutral host offers a pragmatic path to multi-operator mobility with the option to layer private 5G on the same infrastructure. The operational challenge is governance—who owns the SLA, observability, change management, and security segmentation across tenants—making open interfaces and common data models critical.
Tech shifts: 5G SA, edge integration and mmWave reshape the RAN
Technical choices are converging on architectures that bring compute closer to users and unlock 5G-Advanced features at practical cost points.
5G Standalone emerges as the default control plane
SCF expects 5G SA small cells to grow at a 56% CAGR through 2030, reflecting the need for native 5G cores to expose policy, QoS, and slicing to applications. SA simplifies private and hybrid deployments, reduces LTE dependencies, and enables deterministic behavior for industrial workloads. The key design choice is core placement—on-prem for data sovereignty, at the metro edge for latency-sensitive multi-site operations, or operator/cloud-hosted for scale—with integration to enterprise identity and OT systems determining time-to-value.
Edge co-location powers AI-driven enterprise services
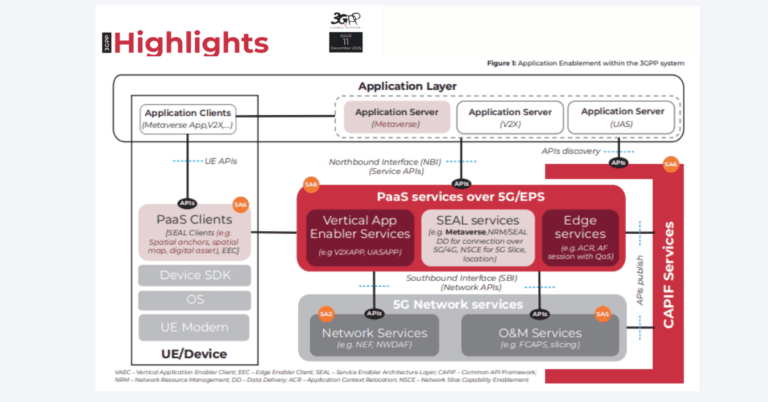
By 2030, SCF anticipates two-thirds of enterprise small cells will be co-located with edge compute, enabling low-latency analytics and closed-loop automation. Typical stacks combine small cells, a 5G SA core, and GPU– or CPU-based edge platforms running AI models for video analytics, digital twins, or quality inspection. ETSI MEC APIs and 3GPP edge enablers are increasingly used for application placement, traffic steering, and exposure of network capabilities to developers. The practical constraint is lifecycle management—software supply chain, model updates, and observability—which argues for consistent CI/CD and zero-touch operations.
mmWave/FR2 scales in dense venues and FWA hot zones
Millimetre wave (FR2) deployments are forecast to represent 43% of new small cells by 2030, growing at nearly 37% CAGR. FR2’s high capacity and short range suit stadiums, transport hubs, campuses, and fixed-wireless access hot zones. Success hinges on radio efficiency, beam management, and site engineering, including street furniture rights, power, and fiber backhaul. Expect multi-band small cells that blend FR1 mid-band for coverage with FR2 for peak throughput, backed by smarter RAN optimization and energy-aware scheduling.
Standards, openness and policy will determine scale
Turning specifications into deployable, repeatable solutions remains the industry’s gating factor—and where cross-industry work is accelerating.
From specs to deployable blueprints
SCF is advancing technical and commercial blueprints for in-building and neutral host deployments, aiming to close gaps between 3GPP features and real-world integration. The emphasis is on end-to-end solution patterns that include RF design, power and backhaul, core placement, security zones, and operational handoffs. These blueprints help reduce venue-by-venue customization and shorten the sales-to-service cycle.
Open interfaces cut integration cost and speed rollout
Interfaces such as FAPI and nFAPI from SCF, O-RAN Alliance open fronthaul, and 3GPP service-based architecture are central to multi-vendor small-cell stacks. They enable mix-and-match radios, distributed/centralized units, and RIC-enabled optimization as software lifecycles decouple from hardware. Vendors that certify against these interfaces and publish telemetry schemas simplify neutral host onboarding and multi-operator acceptance testing.
Policy levers and simplified planning
Regulatory clarity on shared spectrum and streamlined permitting are critical to the forecast. Models like CBRS in the US and local/regional enterprise licensing in parts of Europe have catalyzed private 5G. Planning reforms for in-building systems, standardized multi-operator agreements, and pragmatic EMF guidance can further compress deployment timelines while maintaining safety and coexistence.
Next steps: execution playbooks by stakeholder
With demand signals strengthening, the strategic edge goes to those who productize blueprints, operationalize openness, and measure outcomes in business terms.
For mobile network operators (MNOs)
Scale indoor coverage via neutral host where economics favor sharing, reserving bespoke builds for strategic venues; prioritize 5G SA upgrades and exposure APIs that let enterprises control QoS and security; adopt common RAN sharing constructs (MOCN/MORAN) and acceptance tests to reduce integration cycles; and align edge footprints with metro demand for latency-sensitive use cases.
For neutral hosts and towercos
Productize multi-operator indoor solutions with repeatable RF designs, standardized SLAs, and clear demarcations; co-locate edge compute to enable premium services with revenue-sharing models; build FR1+FR2 roadmaps tied to venue archetypes; and invest in observability platforms that offer per-tenant analytics and energy KPIs.
For enterprises and integrators
Start with a coverage and latency audit mapped to critical workflows; select spectrum strategies that balance availability and control (e.g., shared/local licenses); decide core placement based on data governance and application latency; plan for IT/OT segmentation, identity federation, and zero-trust; and require open-interface compliance in RFPs to avoid lock-in.
For vendors and chipset/software providers
Expand small-cell portfolios to support 5G SA, FR1+FR2, and edge-native observability; certify against FAPI/nFAPI and O-RAN interfaces; optimize for energy per bit and simplified install; and offer lifecycle automation with secure supply-chain controls to ease neutral host scaling.
The throughline is clear: as enterprises demand predictable wireless and operators pursue capital efficiency, shared small-cell infrastructure, 5G SA control planes, and edge intelligence are converging into the default design pattern for the next decade.