Meril Mizzo Endo 4000: AI and 5G drive India’s surgical robotics shift
The newly unveiled soft tissue robotic system blends AI-driven imaging with 5G-enabled telesurgery, reframing how hospitals, networks, and vendors will deliver minimally invasive care.
India’s inflection point: AI- and 5G-enabled surgical robotics
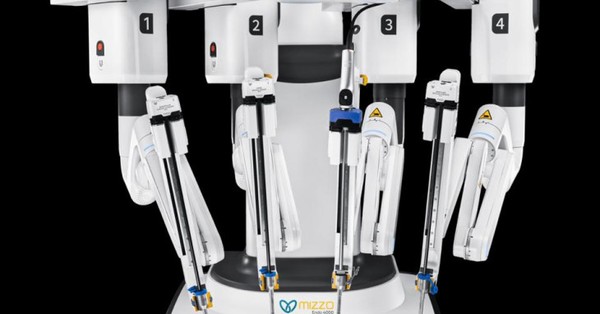
Meril Life Sciences, headquartered in Vapi, Gujarat, has introduced the Mizzo Endo 4000, a soft tissue robotic platform engineered for general, urology, gynecology, thoracic, colorectal, bariatric, hepatobiliary, ENT, gastrointestinal, and oncology procedures. Built and designed in India, the system targets precision, access, and cost barriers that have historically limited adoption. It pairs AI-powered 3D anatomical mapping with an open console design and immersive visualization, while enabling remote collaboration and telesurgery over high-performance 5G networks. Strategically, this positions India to compete with incumbent systems from Intuitive Surgical, Medtronic, and CMR Surgical, while appealing to price-sensitive markets across Asia and Africa.
Why this matters now for healthcare and telecom leaders
Soft tissue robotics is moving beyond a handful of flagship operating rooms into scaled, networked environments. As platforms integrate AI, real-time 3D video, and remote-assist workflows, surgical robotics becomes a distributed digital service dependent on deterministic connectivity, interoperable data pipelines, and secure edge compute. The Mizzo Endo 4000 is an early signal that medtech and telecom roadmaps must converge to make “borderless surgery” clinically safe, affordable, and repeatable.
Mizzo Endo 4000 features: AI imaging, precision arms, 5G telesurgery
The system adds AI-first imaging, precise mechatronics, and OR-friendly integration that collectively lower the barrier to routine soft tissue robotic use.
AI-driven 3D imaging and DICOM-native surgical planning
The platform supports AI-based 3D reconstruction for real-time anatomical mapping, which helps surgeons plan port placement and navigate critical structures. Native DICOM viewing and pre-visualization align with existing PACS/VNA workflows, improving pre-op planning and intra-op guidance without forcing hospitals to overhaul imaging infrastructure. This is meaningful for case throughput, standardization, and training—three adoption bottlenecks in soft tissue robotics.
Precision robotic arms with haptics and OR-friendly integration
Articulated robotic arms are designed for sub-millimeter control and multi-quadrant access, aided by synchronized audio-visual cues and haptic-style feedback to enhance dexterity on delicate tissue. Expect benefits in resections, suturing, and dissection where consistency and tremor reduction matter. A modality-agnostic OR cart and open console approach are intended to streamline integration into existing surgical suites and simplify ergonomics for teams transitioning from laparoscopy.
5G telesurgery and tele-mentoring with deterministic latency
Telesurgery and tele-mentoring are built into the workflow, allowing experts to proctor or intervene remotely when connectivity meets strict latency, bandwidth, and reliability thresholds. This elevates specialist reach to tier-2/3 cities and supports cross-border collaboration. The implication: hospitals will need deterministic performance across video streams, control signals, and telemetry, with local failover and rapid reversion to manual control if conditions degrade.
Network and IT for surgical robots: private 5G, MEC, and resilience
Reliable remote surgical workflows demand converged networking, secure edge compute, and rigorous data interoperability.
Connectivity for robotic ORs: private 5G, URLLC, and network slicing
Private 5G in hospital campuses—paired with fiber backhaul and MEC—offers predictable uplink for multi-stream 3D video and command/response, outperforming best-effort Wi‑Fi in interference-heavy environments. To support remote assistance, operators should design for URLLC-class performance and enforce QoS with network slicing, traffic prioritization, and time synchronization (e.g., PTP) for coordinated video and haptics. Redundancy across dual links and automatic path failover are non-negotiable for safety-critical use.
Data interoperability and cybersecurity: DICOM, HL7/FHIR, zero trust
The system’s DICOM integration should tie cleanly into PACS/VNAs and EMRs via HL7/FHIR, with audit logs and video analytics stored at the edge and tiered to the cloud. Medical software lifecycle and risk management frameworks—such as IEC 62304 and ISO 14971—are relevant to hospital procurement and governance. Given telesurgery’s attack surface, adopt zero-trust access, hardware-based key protection, continuous posture assessment, and segmented networks. In India, data-handling practices must align with emerging health-data guidelines and the Digital Personal Data Protection regime.
Market outlook: competing with da Vinci, Hugo, and Versius
Meril is entering a market shaped by mature incumbents and rising demand for cost-effective, interoperable systems.
Competing with incumbents on cost, imaging, and interoperability
Intuitive’s da Vinci remains the benchmark for installed base and clinical depth, while Medtronic’s Hugo and CMR Surgical’s Versius have pressed on modularity and cost. Meril’s angle is AI-enhanced imaging, native DICOM workflows, and price competitiveness tailored to emerging markets. If the company maintains a lower total cost of ownership—capex plus instruments, service, training—it can unlock utilization in mid-tier hospitals that have avoided robotics due to ongoing costs.
Scaling and export: approvals, training, service, and financing
Scaling depends on regulatory clearances (CDSCO domestically and, over time, MDR/CE and FDA for exports), surgeon training capacity, and a consistent service footprint. Partnerships with teaching hospitals and simulation centers will influence early outcomes. Expect creative financing—leasing, managed services, per-procedure models—to accelerate adoption, particularly where capital is constrained.
Risks and open questions: safety, liability, and connectivity
Clinical efficacy, operational resilience, and legal frameworks will determine how far and how fast telesurgery progresses.
Safety, liability, and operational resilience in telesurgery
Remote operation raises questions about acceptable latency ceilings, shared control handoffs, and cross-border medical licensing. Hospitals should mandate runbooks for connectivity loss, manual takeover, and on-site surgical backup. Human factors—console ergonomics, team communication, and standardized checklists—remain decisive for outcomes regardless of platform sophistication.
Equity and last-mile readiness: SLAs, redundancy, and training
Telesurgery’s promise hinges on stable connectivity beyond metros. Hub-and-spoke models that combine private 5G at tertiary centers with assured links to satellite facilities can extend reach, but only if SLAs, redundancy, and training are in place. Public-private partnerships will be critical to make advanced robotics accessible without widening the digital divide.
Next steps for CIOs and partners: readiness, governance, and SLAs
Early planning around networks, workflows, and governance will separate pilots that scale from demonstrations that stall.
Hospital actions: connectivity audits, training, and open APIs
Run a readiness assessment of OR connectivity, imaging interoperability, and cybersecurity; pilot in high-volume specialties with clear outcome metrics; budget for training, simulation, and sterile supply logistics; and push vendors for open APIs, usage analytics, and guaranteed uptime. Align biomedical engineering, IT, and clinical teams under a single governance model.
Telecom and cloud actions: private 5G/MEC blueprints and SLAs
Co-design private 5G and MEC blueprints for robotic ORs, with deterministic QoS, monitoring, and automated failover; craft healthcare-grade SLAs; integrate DICOM-aware acceleration and secure media pipelines; and build reference architectures with hospital partners to shorten procurement cycles.
Investor focus: evidence, lifecycle costs, and training ecosystems
Track Meril’s clinical evidence, service capacity, and pricing model; develop accessory ecosystems (instruments, vision, analytics); and support training academies that create a durable talent pipeline. Interoperability and lifecycle costs will be the deciding factors in multi-year purchasing decisions.
Bottom line: Meril’s Mizzo Endo 4000 signals a shift toward AI-native, networked surgical robotics, where clinical performance is inseparable from connectivity, data, and operational excellence.