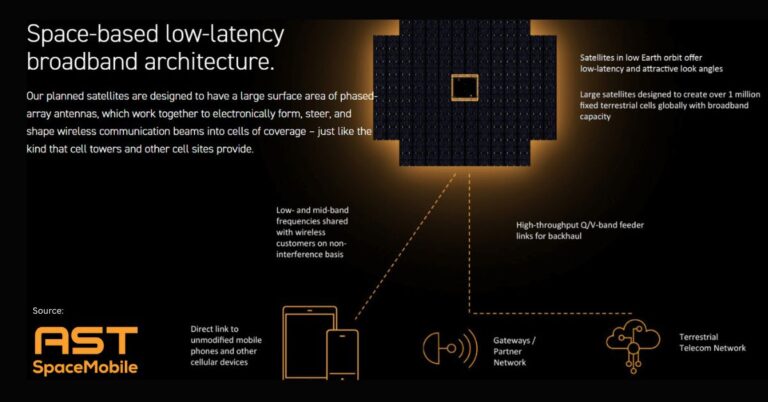
The emergence of Direct-to-Device (D2D) satellite services is a game-changer for global communications, promising to extend coverage to previously unreachable areas and enhance existing terrestrial networks. Despite its transformative potential, the future of D2D depends heavily on navigating the technological, regulatory, and economic challenges associated with spectrum allocation.
The recently released whitepaper by Summit Ridge Group and TMF Associates, “Spectrum for Emerging Direct-to-Device Satellite Operators,” provides a comprehensive analysis of these challenges. It also identifies actionable solutions that could enable the successful deployment of D2D networks worldwide.
Market Trends Driving D2D Satellite Connectivity Growth
The confluence of advancements in satellite design, consumer device miniaturization, and increasing global connectivity demand has created a fertile ground for D2D innovation. Satellite operators, mobile network operators (MNOs), and consumer electronics giants like Apple and SpaceX have recognized the potential of D2D, driving significant investments into this sector.
However, despite the excitement surrounding D2D, the market is fraught with uncertainty:
- Market Size and Viability: The exact market size for D2D remains speculative. Historical challenges with earlier satellite communications ventures, such as Iridium and Globalstar, underscore the risks of overestimating consumer willingness to pay for universal connectivity.
- Business Model Evolution: While some providers aim to offer free D2D services as part of bundled packages (e.g., Apple’s partnership with Globalstar), others focus on monetizing spectrum through enterprise and government applications.
The whitepaper identifies that only a limited number of D2D operators are likely to survive to maturity, particularly given the high capital requirements and spectrum availability constraints. Successful players will be those who strike the right balance between technological innovation, economic feasibility, and user adoption.
Why Spectrum Sharing Falls Short for D2D Satellite Services
While spectrum scarcity is a key hurdle for D2D services, the whitepaper elaborates on why spectrum sharing is impractical in many cases. Unlike higher-frequency Fixed Satellite Services (FSS) bands, where technologies like “arc avoidance” enable effective sharing, the characteristics of MSS spectrum make similar solutions unworkable for D2D:
- Technical Constraints of MSS Bands:
- MSS devices, particularly consumer smartphones, use omnidirectional antennas that cannot avoid interference as effectively as FSS antennas. This increases the risk of overlapping signals in shared spectrum environments.
- D2D services require higher power levels to achieve their desired coverage and capacity, further complicating spectrum sharing with existing MSS users.
- Safety and Critical Services:
- MSS bands like L-band and Big LEO support safety-of-life services, including maritime and aviation communications. Any disruption caused by spectrum sharing would jeopardize these mission-critical applications.
- Priority-Based Sharing:
- Priority mechanisms, such as those used in terrestrial networks (e.g., CBRS), are ill-suited for MSS bands. For instance, emergency D2D services cannot afford to delay or suspend operations due to interference concerns.
The whitepaper stresses that relying on co-frequency sharing will lead to degraded service quality for both MSS incumbents and D2D operators, undermining the reliability of the broader ecosystem.
Why the 2 GHz Band is Vital for Expanding D2D Satellite Services
Among the MSS spectrum bands, the 2 GHz band emerges as a particularly attractive candidate for D2D services. The whitepaper provides an in-depth examination of why this spectrum holds unique advantages:
- Underutilization: Unlike the L-band and Big LEO, which are heavily utilized for safety-critical and commercial services, the 2 GHz band has relatively few active users. This creates an opportunity to allocate significant portions of the spectrum for new D2D deployments without substantial disruption to incumbents.
- Flexibility and Scalability: The 2 GHz band offers greater flexibility for innovative system design. For example, it could support tailored regulatory changes, such as increased power levels, to enhance service delivery without compromising spectrum efficiency.
- Consolidated Holdings: Spectrum in the 2 GHz band is primarily held by a few players, including EchoStar, Inmarsat, and Omnispace. This consolidation simplifies commercial negotiations and accelerates the coordination process needed for D2D deployment.
- Global Availability: Unlike other bands, which are fragmented across regions, the 2 GHz band offers near-global harmonization, facilitating seamless connectivity across borders.
How Partnerships Are Unlocking D2D Spectrum Access
Given the impracticality of spectrum sharing and the competitive constraints of terrestrial spectrum, the whitepaper highlights the pivotal role of commercial agreements between MSS incumbents and D2D operators. Such agreements provide a win-win solution:
- For MSS Operators: They gain new revenue streams by monetizing underutilized spectrum assets.
- For D2D Providers: They acquire the spectrum access needed to meet growing demand for global connectivity.
Examples of successful agreements include:
- Apple and Globalstar: This partnership allocates portions of Globalstar’s Big LEO spectrum for D2D services, enabling emergency messaging on millions of iPhones worldwide.
- AST SpaceMobile and Ligado: AST’s agreement with Ligado to lease 40 MHz of L-band spectrum in the U.S. underscores the potential of leveraging commercial deals to unlock D2D opportunities.
By focusing on the 2 GHz band, the industry can further streamline these agreements, creating a scalable and sustainable model for D2D expansion.
Innovations Powering Next-Gen D2D Satellite Connectivity
While initial D2D deployments are focused on text-based services, the whitepaper emphasizes the technological advancements required to enable voice, data, and even video streaming capabilities. Key innovations include:
- Advanced Satellite Design: Next-generation Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites are being designed to support higher throughput and dynamic spectrum allocation.
- Consumer Device Optimization: Smartphone manufacturers are integrating capabilities for spectrum bands like 2 GHz and L-band, enabling seamless satellite communication without compromising device performance.
- Power Management: Increasing power levels for MSS-based D2D services is critical to overcoming signal propagation challenges and ensuring reliable coverage, even in densely populated areas.
Navigating Regulatory Barriers for D2D Satellite Success
The regulatory environment for D2D is still evolving, with initiatives like the FCC’s Supplementary Coverage from Space (SCS) rules providing a foundation for progress. However, achieving global harmonization remains a challenge due to variations in spectrum policies across regions. The whitepaper advocates for:
- International Coordination: Enhanced collaboration among regulators, MSS operators, and D2D providers to establish consistent spectrum policies.
- Incentivizing Innovation: Offering regulatory incentives to MSS operators willing to support D2D services, such as streamlined licensing processes and financial subsidies for spectrum upgrades.
Paving the Way for Universal Connectivity
The journey to realizing the full potential of D2D services is complex, but the roadmap outlined in the whitepaper offers actionable solutions. By prioritizing the 2 GHz band, fostering commercial partnerships, and investing in technological innovation, the satellite and telecom industries can address the spectrum challenges that currently hinder D2D scalability.
Direct-to-Device represents a paradigm shift in global connectivity, with the potential to connect billions of devices and bridge digital divides. The success of this vision will depend on the industry’s ability to navigate spectrum dynamics effectively and establish a robust framework for collaboration and innovation.
For more insights, access the full whitepaper at Summit Ridge Group’s Whitepaper.