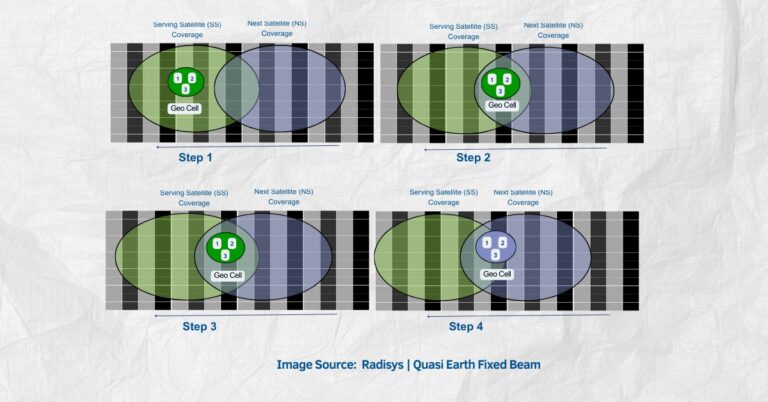
London, 19 October 2023 – Eutelsat OneWeb, part of the Eutelsat Group, the satellite communications company, confirmed today that its low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellation has successfully connected to a 5G mobile network, supporting 5G QoS levels for the first time. This milestone brings super-fast mobile phone connectivity to remote and rural areas one step closer.
The achievement of successful 5G tests can be attributed to the Sunrise Programme, a partnership supported by the European Space Agency. This initiative aims to unite the industry around large-scale programmes, fostering significant advancements and driving economic growth. Through the demonstration, the University of Surrey tested a 5G mobile network by connecting Surrey’s 5G core to a cell site through the LEO constellation, which consists of over 600 satellites in orbit and is the second-largest constellation globally.
Over the constellation-assisted connection, researchers tested video conferencing calls, video streaming, gaming, virtual and augmented reality content, and simple web browsing. With a LEO constellation, the service can deliver low-latency connectivity coupled with high speeds to enable these applications. Tests also highlighted a seamless, smooth handover between the LEO network and terrestrial networks, delivering a smooth 5G connectivity experience to users.
Barry Evans, Professor of Satellite Communications at the 6G/5G Innovation Centre (6G/5GIC) at the University of Surrey, said: “It was thrilling to see no degradation when using the 5G connection made possible by the LEO constellation. This is a step closer to increasing internet access for more people around the world – a privilege that many of us take for granted. “The work performed in the 5G pilot tests has demonstrated the feasibility of 5G backhaul over LEO satellites.”
Eutelsat OneWeb’s connectivity works by using a system similar to 4G. Surrey researchers matched 5G quality levels in the mobile network with 4G quality levels in the LEO network. This enabled end-to-end support for all the applications trialed in the project.
Eutelsat OneWeb, part of Eutelsat Group, which includes the UK Government as one of its strategic shareholders, recently signed a deal with Telstra in Australia to backhaul their 4G and 5G networks.
Professor Rahim Tafazolli, Director of the Institute for Communication Systems at the University of Surrey, added, “It is a fantastic achievement from different perspectives. Surrey’s standard-compliant 5G Core works perfectly with large constellation satellite and terrestrial networks. We are delighted to see the UK taking the lead in space/terrestrial network convergence and solving digital divide challenges as we work towards ubiquitous high-quality coverage of broadband services.”
Massimiliano Ladovaz, Eutelsat Group Chief Operations Officer, added: “We are delighted to have collaborated with the University of Surrey and ESA on these 5G pilot tests, which underscored the huge potential of our LEO services for serving mobile users in rural and remote areas. As we continue to deliver for our existing customers and look forward to activating global coverage later this year, our driving focus will continue to revolve around expanding access to connectivity around the world.”
Javier Benedicto, Acting Director of Connectivity and Secure Communications at ESA, said: “We are proudly celebrating today our cooperation, under the Sunrise Partnership Project, with a large telecommunications operator such as Eutelsat OneWeb and its partners, including small and medium-sized enterprises and academia. By working in a lean style using commercial off-the-shelf components and flexible project management to bring innovative technologies to market in response to commercial needs, ESA is helping to foster innovation in 5G connectivity in the highly competitive global market for telecommunications satellites.”
Harshbir Sangha, Missions and Capabilities Delivery Director at the UK Space Agency, said: “It’s fantastic to see the LEO network successfully connect to a 5G mobile network. This achievement demonstrates the huge potential of its innovative technology to enhance connectivity and improve people’s lives, whether that means better broadband services in remote places or the ability to respond more effectively to emergency situations.”
Source: Press releases Read More