- Tech News & Insight
- November 24, 2025
- Hema Kadia
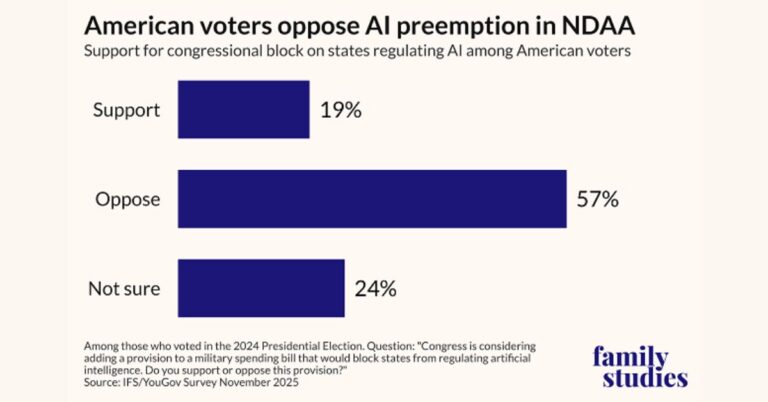
Policy
- Tech News & Insight
- November 21, 2025
- Hema Kadia
Ericsson’s latest Mobility Report points to a clear shift: operators are turning 5G capabilities into differentiated, SLA-backed services rather than just selling more data at higher speeds. After years of building coverage and capacity, 5G networks are mature enough to commercialize features like guaranteed latency, uplink boosts, and application-aware prioritization.
- Tech News & Insight
- November 21, 2025
- Hema Kadia
India’s 5G market has entered a scale phase, with momentum pointing to more than a billion subscribers and deeper network modernization over the next six years. Ericsson’s latest Mobility Report projects over 1 billion 5G subscriptions in India by end-2031, representing about 79% of the country’s mobile base. Average mobile
- Tech News & Insight
- December 3, 2025
- Hema Kadia
Nvidia’s latest quarter signals that AI infrastructure spending is not cooling and is, in fact, broadening across clouds, sovereigns, and enterprises. Nvidia delivered $57 billion in revenue for the quarter, up more than 60% year over year, with GAAP net income reaching $32 billion; the data center segment accounted for
- Tech News & Insight
- December 3, 2025
- Hema Kadia
Palo Alto Networks is buying Chronosphere to fuse cost-efficient, large-scale observability with AI-driven automation for modern cloud and AI data centers. Palo Alto Networks agreed to acquire Chronosphere for approximately $3.35 billion in a mix of cash and replacement equity, with closing expected in the second half of PANW’s fiscal
- Tech News & Insight
- November 20, 2025
- Hema Kadia
Airbus Defence and Space has introduced Agnet Direct, a multi-mode extension to its 3GPP-based Agnet portfolio that keeps teams connected when commercial or private 4G/5G coverage is compromised. Agnet Direct has been validated within France’s Réseau Radio du Futur (RRF), the nationwide secure broadband network for domestic security and emergency
- Tech News & Insight
- November 19, 2025
- Hema Kadia
Nokia is restructuring to monetize the AI supercycle across fixed and mobile networks while tightening focus on profitable growth. The company’s new strategy concentrates on: accelerating in AI and cloud; leading the next era of mobile with AI-native networks and 6G; co-innovating with customers and partners; concentrating capital where it
- Tech News & Insight
- November 19, 2025
- Hema Kadia
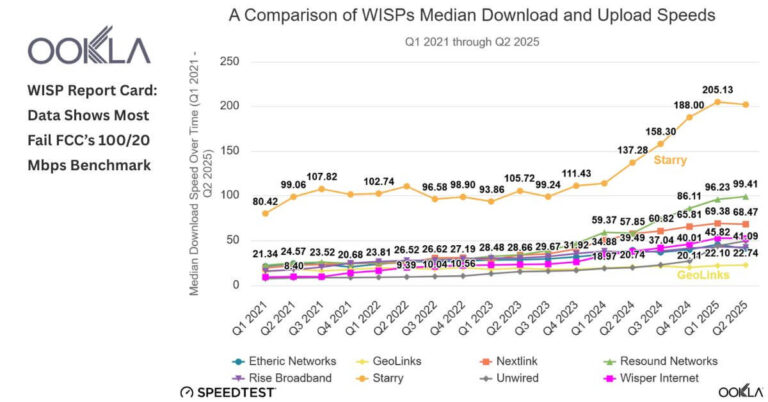
New performance data shows U.S. WISPs are getting faster, but low‑Earth orbit players like Starlink are advancing just as quickly—and the competitive gap in rural markets is narrowing. Based on Speedtest Intelligence data from Q1 2021 to Q2 2025, eight of the larger WISPs—Starry, Resound Networks, Nextlink, Wisper Internet, Unwired
- Tech News & Insight
- November 18, 2025
- Hema Kadia
A new impact study shows CTIA Wireless Foundation’s Catalyst program has touched 30 million Americans since 2019, underscoring how mobile-first tools can scale social outcomes faster than traditional interventions. The Foundation has invested just over $1 million in unrestricted grants yet reports benefits to nearly one in 12 Americans—evidence of
- Tech News & Insight
- November 17, 2025
- Hema Kadia
Cisco’s intent to acquire Seattle-based NeuralFabric signals a decisive shift toward practical, domain-specific AI that meets real-world constraints around data, compliance, and infrastructure. Cisco plans to acquire NeuralFabric, an enterprise AI platform focused on building small language models (SLMs) from proprietary data with deployment across SaaS and on-premises environments. By
- Tech News & Insight
- November 17, 2025
- Hema Kadia
S&P Global Ratings has upgraded Bharti Airtel on the back of stronger earnings quality, healthier free cash flow, and a clearer deleveraging path, signaling a maturing Indian mobile market. The action reflects rising confidence that India’s tariff repair is sticking after mid-2024 hikes, with average revenue per user moving up
- Tech News & Insight
- November 16, 2025
- Hema Kadia
The Las Vegas Grand Prix is more than a spectacle this year—it’s a real-world benchmark for what 5G Standalone can deliver under extreme density, with T-Mobile integrating slicing, private 5G and edge video into broadcast, venue ops and public safety workflows. Broadcast teams are ingesting 360-degree and drone feeds over
TeckNexus Newsletters
I acknowledge and agree to receive TeckNexus communications in line with the T&C and privacy policy.
Whitepaper
Explore RADCOM's whitepaper 'Unleashing the Power of 5G Analytics' to understand how telecom operators can drive cost savings and revenue with 5G. Learn about NWDAF's role in network efficiency, innovative use cases, and analytics monetization strategies. Download now for key insights into optimizing 5G network performance....

Whitepaper
Explore the Private Network Edition of 5G Magazine, your guide to the latest in private 5G/LTE and CBRS networks. This edition spotlights 11 award categories including private 5G/LTE leader, neutral host leader, and rising startups. It features insights from industry leaders like Jason Wallin of John Deere and an analysis...

Check Private Network Readiness
Industry Vertical Specific Deep-Dive Assessment

Manufacturing
$750
250 questions based assessment and insights
$750
Utilities
$500
65+ questions based assessment and insights
$500
Mining
$500
160 questions based assessment and insights
$500
Aviation
Coming Soon
75+ questions based assessment and insights
Coming Soon
Ports
Coming Soon
75+ questions based assessment and insights
Coming Soon* Prices does not include tax