5G to accelerate cellular IoT through 2035
New data points to a step-change in cellular IoT adoption as 5G broadens into mid-tier and massive-scale use cases while 4G-era LPWA keeps expanding.
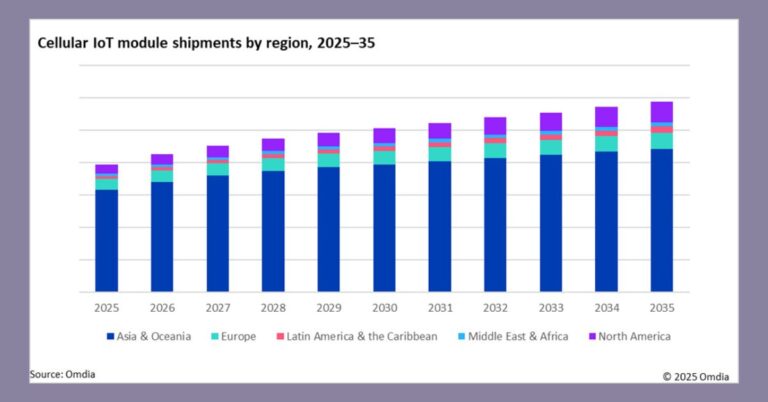
Cellular IoT to reach 5.9B connections by 2035
Omdia forecasts cellular IoT connections to reach roughly 5.9 billion by 2035, driven by expanding addressable use cases across industrial automation, utilities, transportation, retail, and consumer-adjacent categories such as wearables. The growth profile is no longer tied only to premium 5G performance; instead, scaled adoption is coming from three complementary pillars: 5G RedCap for mid-tier performance at lower cost, 5G Massive IoT (evolving NB-IoT/LTE-M under a 5G core), and 4G LTE Cat-1bis for low-cost devices that still require voice or moderate throughput. Asia and Oceania are set to lead several high-growth segments, notably automotive, where consumer demand for intelligent, software-defined vehicles is intensifying.
Three pillars: RedCap, Massive IoT, LTE Cat-1bis
5G RedCap (NR-Light, 3GPP Release 17) fills the gap between LPWA and full 5G eMBB/URLLC, enabling reliable mid-tier throughput, lower latency than LPWA, and better longevity as 4G sunsets begin after 2030. Massive IoT based on NB-IoT and LTE-M continues to scale for ultra-low power, long-life deployments and is integrating with 5G cores for future-proofing. LTE Cat-1bis, a simplified single-antenna variant of Cat-1, remains a cost-effective option for voice-capable or mobility-centric devices where NB-IoT/LTE-M coverage is variable.
Why 5G RedCap matters for IoT now
Enterprises and OEMs need a mid-tier cellular option that lowers module cost and power consumption without sacrificing longevity or quality of service.
Mid-tier 5G performance at lower cost
RedCap is engineered for devices that do not need ultra-low latency or high bandwidth but do require better responsiveness and feature support than LPWA offers, including enhanced mobility, positioning, and QoS options. Because RedCap targets reduced complexity, module pricing and power budgets can be significantly lower than full 5G, making it attractive for industrial sensors, telematics, wearables, cameras with modest bitrates, and connected equipment. Critically, RedCap rides the 5G roadmap, giving buyers a clearer path through 4G refarming later in the decade.
Early RedCap momentum in wearables and industry
Momentum improved with RedCap support in the latest Apple Watch range, catalyzing broader ecosystem investment and operator enablement. On the industrial side, China Mobile’s large RedCap deployment at a smart factory in Hangzhou showcases autonomous guided vehicles and machine tools operating on a high-reliability, low-latency 5G SA network—illustrating how RedCap can meet industrial IoT requirements at lower cost than full 5G modules. Automotive suppliers are also validating RedCap chipsets from Qualcomm and others for next-gen telematics, covering navigation, diagnostics, OTA updates, and basic infotainment.
LPWA scaling with NB-IoT and LTE-M case studies
NB-IoT and LTE-M continue to win where battery life, coverage, and unit economics are paramount.
Logistics and rail IoT
Deutsche Telekom expanded NB-IoT and LTE-M across German Rail to connect cargo units, maintenance tools, and infrastructure sensors, improving asset visibility and condition monitoring across a geographically dispersed network. These LPWA technologies extended reach beyond short-range radios, reducing blind spots and manual interventions.
Utilities and smart grid IoT
AT&T’s LTE-M footprint underpins millions of smart meters for Southern Company, supporting stable, low-power telemetry for load balancing, outage management, and remote diagnostics. This pattern—long-life meters with intermittent, predictable traffic—is an archetypal LTE-M win.
Agriculture and remote asset monitoring
Vodafone’s NB-IoT deployments in European vineyards use soil and climate sensors to optimize irrigation and crop quality while sustaining multi-year battery life. In Australia, Ericsson and Telstra support NB-IoT cattle tracking across remote areas, enabling location and health monitoring with minimal site visits.
Retail payments and POS connectivity
Orange Business Services broadened its LTE-M portfolio for retail and unattended payment, where mobility, high availability, and strong security are table stakes for POS terminals and vending systems deployed at scale.
Automotive IoT outlook and growth drivers
Automotive IoT is set to be one of the fastest-growing cellular segments through the next decade.
Connected vehicles: 500M to 1.2B by 2035
Omdia projects connected vehicle subscriptions to rise from about 500 million today to roughly 1.2 billion by 2035, lifting automotive’s share of all cellular IoT from 13 percent to around 21 percent. The shift to software-defined vehicles, pervasive OTA updates, and regulatory mandates for safety and telematics will drive sustained connectivity demand, with Asia and Oceania contributing a large portion of the growth.
RedCap modules for automotive telematics
Automakers are adopting cost-optimized 5G via RedCap chipsets from Qualcomm and other suppliers to support core telematics functions without the power and cost overhead of full 5G. RedCap’s sweet spot aligns well with mainstream models and trim levels, enabling high attach rates while future-proofing against 4G phase-out.
5G IoT roadmap: what to watch in 2026–2028
Technology milestones and network readiness over the next three years will shape buying decisions and deployment models.
eRedCap and 5G SA readiness for IoT
Enhanced RedCap (expected with 3GPP Release 18 capabilities) should further reduce device complexity and power while broadening mid-tier options, but commercial impact depends on the pace of 5G Standalone rollouts, RedCap feature activation, and module pricing from major vendors. Enterprises should validate RedCap coverage, mobility, and power profiles in target geographies before committing to volume.
4G sunsets and Cat-1bis as a bridge
As operators plan 4G refarming after 2030, Cat-1bis remains a pragmatic bridge for many devices that need voice, voice fallback, or ubiquitous mobility today. Suppliers should design modular SKUs that allow migration from Cat-1bis to RedCap or LTE-M/NB-IoT without redesigning the entire product.
IoT roaming, certification, and security
NB-IoT roaming is improving but remains inconsistent across markets; multi-IMSI eSIM/eUICC with SGP.32 IoT profiles can help. Certification complexity persists for RedCap on 5G SA; plan time for device testing and regional approvals. Strengthen security with IoT SAFE or equivalent hardware root of trust, TLS by default, and cloud/device posture management.
Strategy recommendations for operators and enterprises
Operators and enterprises should align technology roadmaps with coverage, cost, and lifecycle realities to avoid shocks from network transitions.
For operators: 5G IoT priorities
– Accelerate 5G SA and RedCap feature readiness, including power-saving and positioning, and publish clear device certification paths.
– Offer tiered IoT connectivity (NB-IoT/LTE-M/RedCap/Cat-1bis) with transparent SLAs, pricing, and migration assistance ahead of 4G refarming.
– Improve LPWA roaming footprints and service assurance; expose APIs for device lifecycle, QoS, and location.
– Package private 5G for industry with RedCap support, edge computing options, and managed services for industrial integration.
For enterprises and OEMs: IoT playbook
– Segment your portfolio by power, throughput, mobility, and longevity; map each SKU to NB-IoT, LTE-M, Cat-1bis, or RedCap accordingly.
– Pilot RedCap now in factories, telematics, and wearables; measure module power profiles, attach rates, mobility, and TCO against LTE-M and Cat-1bis.
– Use eUICC with SGP.32 for at-scale provisioning; design for remote updates, anomaly detection, and zero-trust device access.
– In regulated and safety-critical applications (automotive, energy), plan for dual connectivity paths and rigorous certification timelines.
– Where coverage is sparse, consider private 5G or hybrid architectures that combine LPWA for telemetry and RedCap for higher-value events.
The bottom line: with RedCap maturing, LPWA scaling, and Cat-1bis anchoring today’s deployments, cellular IoT is entering a sustained growth phase—enterprises that architect now for multi-bearer flexibility and long-term support will be best positioned through the 2030s.